Difference between revisions of "Mucinous breast carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+images) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| Tx = | | Tx = | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Mucinous breast carcinoma''' is an uncommon form of breast cancer that has a good prognosis compared to the common [[ductal | '''Mucinous breast carcinoma''' is an uncommon form of breast cancer that has a good prognosis compared to the common [[Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast|invasive ductal carcinoma]]. | ||
It is also known as '''mucinous carcinoma of the breast''', and '''colloid carcinoma of the breast'''. | It is also known as '''mucinous carcinoma of the breast''', and '''colloid carcinoma of the breast'''. | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 14 February 2014
| Mucinous breast carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
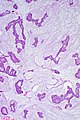
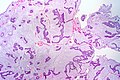
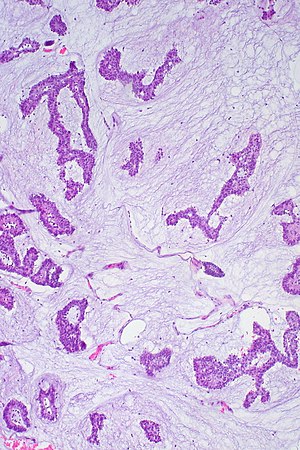 Mucinous breast carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | malignant mucin producing glands - where mucinous component must comprise >90% of the tumour, tumour cells should float in the mucin, glands typically have irregular edges, +/-vessels within the mucin pools |
| LM DDx | other type of breast cancer with a mucinous component (very common), other mucinous tumours |
| IHC | ER +ve, PR +ve, HER2 -ve |
| Gross | pale, glistening, jelly-like appearance |
| Site | breast - see invasive breast cancer |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | good compared to usu. ductal carcinoma |
| Clin. DDx | other breast tumours |
Mucinous breast carcinoma is an uncommon form of breast cancer that has a good prognosis compared to the common invasive ductal carcinoma.
It is also known as mucinous carcinoma of the breast, and colloid carcinoma of the breast.
General
- Rare.
- Good prognosis.[1]
- Usually older women.
Gross
- Pale, glistening, jelly-like appearance.
- Well-circumscribed.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
- Malignant mucin producing glands.
- Mucinous component must comprise >90% of the tumour - required for diagnosis.[2]
- Cells should float in the mucin - key feature.
- Glands typically have irregular edges.
- +/-Vessels within the mucin pools.
DDx:
- DCIS with a mucinous component.
- Mucin has a homogenous appearance, mucin lacks vascularization, mucin pools have a regular border.
Note:
- The amount of mucinous component to call mucinous carcinoma varies by anatomical site.
- All mucinous lesions should be excised.[3]
Images
IHC
- ER +ve.
- PR +ve.
- HER2 -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Barkley, CR.; Ligibel, JA.; Wong, JS.; Lipsitz, S.; Smith, BL.; Golshan, M. (Oct 2008). "Mucinous breast carcinoma: a large contemporary series.". Am J Surg 196 (4): 549-51. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.06.013. PMID 18809061.
- ↑ Dogan, E.; Aksoy, S.; Dizdar, O.; Arslan, C.; Dede, DS.; Ozisik, Y.; Altundag, K.. "Pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast: a single center experience.". J BUON 16 (3): 565-7. PMID 22006768.
- ↑ Jacobs, TW.; Connolly, JL.; Schnitt, SJ. (Sep 2002). "Nonmalignant lesions in breast core needle biopsies: to excise or not to excise?". Am J Surg Pathol 26 (9): 1095-110. PMID 12218567.