Difference between revisions of "Nodular fasciitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
(split-out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Nodular fasciitis''' is an uncommon [[soft tissue lesion]]. It should '''not''' to be confused with [[necrotizing fasciitis]]. | |||
===General=== | |||
*Benign. | |||
*All age groups. | |||
*Associated with trauma. | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
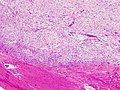
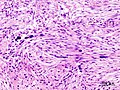
Features:<ref name=Ref_WMSP606>{{Ref WMSP|606}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=de Feraudy S, Fletcher CD |title=Intradermal nodular fasciitis: a rare lesion analyzed in a series of 24 cases |journal=Am. J. Surg. Pathol. |volume=34 |issue=9 |pages=1377–81 |year=2010 |month=September |pmid=20716998 |doi=10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181ed7374 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Usu. well-circumscribed. | |||
*Clusters of (non-pleomorphic) spindle cells. | |||
*Inflammation (lymphocytes). | |||
*Microcysts in cellular regions - uncommon - ''discriminatory''. | |||
*Mitoses - common. | |||
*[[Extravasated RBC]]s. | |||
The BD feature list:<ref>Dickson, B. 26 April 2011.</ref><ref>URL: [http://anvita.info/wiki/Nodular_Fasciitis http://anvita.info/wiki/Nodular_Fasciitis]. Accessed on: 11 November 2011.</ref> | |||
*Tissue culture-like/CNS-like morphology. | |||
*Thick (keloid-like) collagen bundles - '''key feature'''. | |||
*[[Extravasated RBCs]]. | |||
*Inflammation. | |||
*+/-[[Giant cell]]s. | |||
Notes: | |||
*No significant nuclear atypia. | |||
*No atypical mitoses. | |||
*May be cellular. | |||
DDx:<ref>URL: [http://www.mckeedermpath.com/SPOT%20DIAGNOSIS%20CASE%20268.html http://www.mckeedermpath.com/SPOT%20DIAGNOSIS%20CASE%20268.html]. Accessed on: 11 November 2011.</ref> | |||
*Myxoid [[DFSP]]. | |||
*Cellular [[dermatofibroma]]. | |||
*[[Desmoid-type fibromatosis]]. | |||
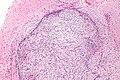
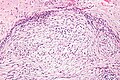
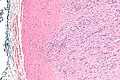
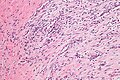
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Nodular_fasciitis_-_intermed_mag.jpg | NF - case 1 - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Nodular_fasciitis_-_high_mag.jpg | NF - case 1 - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Nodular_fasciitis_-2-_intermed_mag.jpg | NF - case 2 - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Nodular_fasciitis_-2-_high_mag.jpg | NF - case 2 - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Nodular_fasciitis_%281%29.JPG | NF - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Nodular_fasciitis_%282%29.JPG | NF - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.humpath.com/nodular-fasciitis NF (humpath.com)]. | |||
===IHC=== | |||
Routine spindle cell panel: | |||
*CD34 -ve. | |||
*Desmin -ve. | |||
*SMA -ve. | |||
*S100 -ve. | |||
*AE1/AE3 -ve. | |||
Others: | |||
*H-caldesmon -ve. | |||
*EMA -ve. | |||
*Vimentin +ve. | |||
===Molecular=== | |||
*Evolving - case reports. | |||
**t(15;15)(q13;q25).<ref name=pmid12606136>{{cite journal |author=Velagaleti GV, Tapper JK, Panova NE, Miettinen M, Gatalica Z |title=Cytogenetic findings in a case of nodular fasciitis of subclavicular region |journal=Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. |volume=141 |issue=2 |pages=160–3 |year=2003 |month=March |pmid=12606136 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumours]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumours]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Revision as of 02:58, 29 September 2013
Nodular fasciitis is an uncommon soft tissue lesion. It should not to be confused with necrotizing fasciitis.
General
- Benign.
- All age groups.
- Associated with trauma.
Microscopic
- Usu. well-circumscribed.
- Clusters of (non-pleomorphic) spindle cells.
- Inflammation (lymphocytes).
- Microcysts in cellular regions - uncommon - discriminatory.
- Mitoses - common.
- Extravasated RBCs.
- Tissue culture-like/CNS-like morphology.
- Thick (keloid-like) collagen bundles - key feature.
- Extravasated RBCs.
- Inflammation.
- +/-Giant cells.
Notes:
- No significant nuclear atypia.
- No atypical mitoses.
- May be cellular.
DDx:[5]
- Myxoid DFSP.
- Cellular dermatofibroma.
- Desmoid-type fibromatosis.
Images
www:
IHC
Routine spindle cell panel:
- CD34 -ve.
- Desmin -ve.
- SMA -ve.
- S100 -ve.
- AE1/AE3 -ve.
Others:
- H-caldesmon -ve.
- EMA -ve.
- Vimentin +ve.
Molecular
- Evolving - case reports.
- t(15;15)(q13;q25).[6]
See also
References
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 606. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ de Feraudy S, Fletcher CD (September 2010). "Intradermal nodular fasciitis: a rare lesion analyzed in a series of 24 cases". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 34 (9): 1377–81. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181ed7374. PMID 20716998.
- ↑ Dickson, B. 26 April 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://anvita.info/wiki/Nodular_Fasciitis. Accessed on: 11 November 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.mckeedermpath.com/SPOT%20DIAGNOSIS%20CASE%20268.html. Accessed on: 11 November 2011.
- ↑ Velagaleti GV, Tapper JK, Panova NE, Miettinen M, Gatalica Z (March 2003). "Cytogenetic findings in a case of nodular fasciitis of subclavicular region". Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 141 (2): 160–3. PMID 12606136.