Difference between revisions of "Traditional serrated adenoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(more) |
(tweak) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
| ClinDDx = | | ClinDDx = | ||
}} | }} | ||
''' | '''Traditional serrated adenoma''', abbreviated '''TSA''', are a rare type of [[gastrointestinal polyp]]. | ||
Before the [[sessile serrated adenoma]]s were recognized, these lesions were known as '''[[serrated adenoma]]s'''.<ref name=pmid20656251>{{Cite journal | last1 = Noffsinger | first1 = AE. | last2 = Hart | first2 = J. | title = Serrated adenoma: a distinct form of non-polypoid colorectal neoplasia? | journal = Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am | volume = 20 | issue = 3 | pages = 543-63 | month = Jul | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1016/j.giec.2010.03.012 | PMID = 20656251 }}</ref> | Before the [[sessile serrated adenoma]]s were recognized, these lesions were known as '''[[serrated adenoma]]s'''.<ref name=pmid20656251>{{Cite journal | last1 = Noffsinger | first1 = AE. | last2 = Hart | first2 = J. | title = Serrated adenoma: a distinct form of non-polypoid colorectal neoplasia? | journal = Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am | volume = 20 | issue = 3 | pages = 543-63 | month = Jul | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1016/j.giec.2010.03.012 | PMID = 20656251 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist| | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | [[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | ||
Revision as of 09:20, 29 July 2013
| Traditional serrated adenoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 | |
|
| |
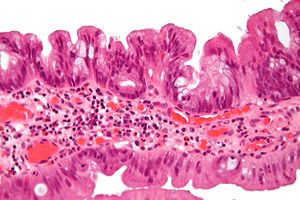
| LM | serrated, eosinophilic cytoplasm, villous-like architecture |
| LM DDx | villous adenoma |
| Site | colon - usu. left side / gastrointestinal polyps |
|
| |
Traditional serrated adenoma, abbreviated TSA, are a rare type of gastrointestinal polyp.
Before the sessile serrated adenomas were recognized, these lesions were known as serrated adenomas.[1]
General
- Very rare.
- Pre-malignant.[2]
Gross
- Polypoid mass.
- Usually in the left colon.
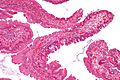
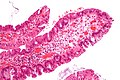
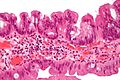
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Serrated - essential.
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm - key feature.
- Nuclear atypia as in tubular adenoma.
- Nuclear hyperchromasia, enlargement and pseudostratification.
- Villous-like architecture.
DDx:
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Noffsinger, AE.; Hart, J. (Jul 2010). "Serrated adenoma: a distinct form of non-polypoid colorectal neoplasia?". Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 20 (3): 543-63. doi:10.1016/j.giec.2010.03.012. PMID 20656251.
- ↑ Rosty, C.; Hewett, DG.; Brown, IS.; Leggett, BA.; Whitehall, VL. (Mar 2013). "Serrated polyps of the large intestine: current understanding of diagnosis, pathogenesis, and clinical management.". J Gastroenterol 48 (3): 287-302. doi:10.1007/s00535-012-0720-y. PMID 23208018.
- ↑ Li SC, Burgart L (March 2007). "Histopathology of serrated adenoma, its variants, and differentiation from conventional adenomatous and hyperplastic polyps". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 131 (3): 440-5. PMID 17516746. http://journals.allenpress.com/jrnlserv/?request=get-abstract&issn=0003-9985&volume=131&page=440.