Difference between revisions of "Pulmonary carcinoid tumourlet"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+syndrome) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| Site = [[lung]] - see ''[[lung tumours]]'' | | Site = [[lung]] - see ''[[lung tumours]]'' | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Syndromes = [[ | | Syndromes = [[Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia]] | ||
| Clinicalhx = often an incidental finding | | Clinicalhx = often an incidental finding | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = | ||
Latest revision as of 03:30, 22 March 2018
| Pulmonary carcinoid tumourlet | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
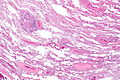
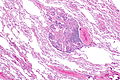
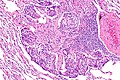
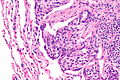
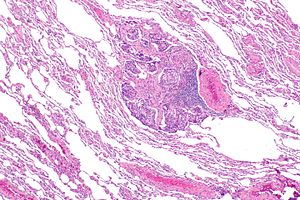 Lung carcinoid tumourlet. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | carcinoid tumourlet |
|
| |
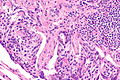
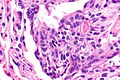
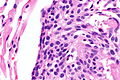
| LM | cells with salt and pepper chromatin, usually nested architecture, no necrosis, minimal mitotic activity (see below), must be through the bronchial basement membrane |
| LM DDx | pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia, typical carcinoid lung tumour, atypical lung carcinoid tumour, pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule |
| IHC | Ki-67 ~2% (0-7%) |
| Gross | <5 mm by definition |
| Site | lung - see lung tumours |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia |
|
| |
| Clinical history | often an incidental finding |
| Prevalence | not common |
| Prognosis | benign |
Pulmonary carcinoid tumourlet, also carcinoid tumourlet, is a small benign proliferation of Kulchitsky cells.
The entity is separated from the typical lung carcinoid tumour by size. Carcinoid tumourlets are < 5 mm, typical lung carcinoid tumours are >=5 mm.
General
- Neuroendocrine cell proliferation.[1]
- Essentially a small typical carcinoid.
- Arise from Kulchitsky cells of the bronchial epithelium.[2]
- May be seen in the context of diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia.
Microscopic
Features:
- Neuroendocrine cells - usually in nests (classic pattern).
- Salt and pepper chromatin - key feature.
- Nuclei round or ellipsoid.
- Size criterion: <5 mm.[3][4]
- Must be through the bronchial basement membrane.[5]
DDx:
- Pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia - proliferation confined by bronchial basement membrane.[5]
- Typical carcinoid lung tumour - must be >= 5 mm.
- Pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule - whorled appearance, not associated with an airway.
Images
www:
Sign out
A. Lymph Node, Station 4R, Lymphadenectomy: - Lymph node, NEGATIVE for malignancy. B. Lymph Node, Station 11R, Lymphadenectomy: - Lymph node, NEGATIVE for malignancy. C. Lung, Right Middle Lobe, Lobectomy: - Typical carcinoid tumour (13 mm maximal dimension). - Carcinoid tumourlet (3 mm maximal dimension). - Margins clear of tumour. - Please see tumour summary.
See also
References
- ↑ Bennett, GL.; Chew, FS. (Mar 1994). "Pulmonary carcinoid tumorlets.". AJR Am J Roentgenol 162 (3): 568. PMID 8109497.
- ↑ Ramón Capilla, M.; Arnau Obrer, A.; Navarro Ibáñez, R.; Galbis Caravajal, J.; Traves Zapata, V.; Cantó Armengod, A. (Nov 1996). "[Pulmonary tumorlet. Report of 5 cases].". Arch Bronconeumol 32 (9): 489-91. PMID 9064089.
- ↑ URL: http://pathhsw5m54.ucsf.edu/case7/image75.html. Accessed on: 23 January 2012.
- ↑ He, P.; Gu, X.; Wu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Gu, Y.; He, J. (Dec 2012). "Pulmonary carcinoid tumorlet without underlying lung disease: analysis of its relationship to fibrosis.". J Thorac Dis 4 (6): 655-8. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2012.06.11. PMID 23205296.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Koo, CW.; Baliff, JP.; Torigian, DA.; Litzky, LA.; Gefter, WB.; Akers, SR. (Sep 2010). "Spectrum of pulmonary neuroendocrine cell proliferation: diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia, tumorlet, and carcinoids.". AJR Am J Roentgenol 195 (3): 661-8. doi:10.2214/AJR.09.3811. PMID 20729444.