Difference between revisions of "Endolymphatic sac tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (pictures + infobox) |
(tweak formating, wikifying) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| Micro = Papillary epithelial structures. | | Micro = Papillary epithelial structures. | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[ | | LMDDx = [[choriod plexus papilloma]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = CK7 +ve | | IHC = CK7 +ve | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Choroid plexus papilloma - when infiltrating cerebellopontine angle via petrous bone | *[[Choroid plexus papilloma]] - when infiltrating cerebellopontine angle via petrous bone. | ||
*Metastatic [[adenocarcinoma]] | *[[Metastatic]] [[adenocarcinoma]]. | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
*CK7 +ve | *CK7 +ve. | ||
*S-100 +ve (focally) | *S-100 +ve (focally). | ||
*CD31 +ve - marks the outline of the papillary structures.<ref name=pmid24966979/> | *CD31 +ve - marks the outline of the papillary structures.<ref name=pmid24966979/> | ||
*Kir 7.1-ve - discriminates | *Kir 7.1-ve - discriminates tumour from plexus papilloma.<ref name=pmid22706862>{{Cite journal | last1 = Schittenhelm | first1 = J. | last2 = Roser | first2 = F. | last3 = Tatagiba | first3 = M. | last4 = Beschorner | first4 = R. | title = Diagnostic value of EAAT-1 and Kir7.1 for distinguishing endolymphatic sac tumors from choroid plexus tumors. | journal = Am J Clin Pathol | volume = 138 | issue = 1 | pages = 85-9 | month = Jul | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1309/AJCPPRKNNL09JTLP | PMID = 22706862 }}</ref> | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 05:20, 29 April 2015
| Endolymphatic sac tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
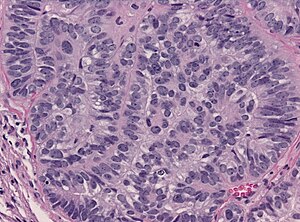 Endolymphatic sac tumor H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | Papillary epithelial structures. |
| LM DDx | choriod plexus papilloma |
| IHC | CK7 +ve |
| Site | usually inner ear |
|
| |
| Symptoms | Tinnitus, dizziness |
| Prevalence | very rare |
| Prognosis | locally agressive |
Endolymphatic sac tumour, abbreviated ELST, is a very rare tumour associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease.
General
- Rare.
- Locally aggressive.[1]
- Associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease.
- May be sporadic.[1]
Clinical - common:[2]
- Hearing loss (sensorineural).
- Tinnitus.
- Dizziness.
Treatment:
- Surgical excision.[2]
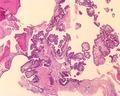
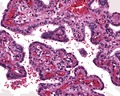
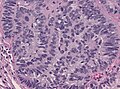
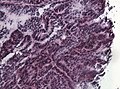
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Cystic spaces.
- Papillary structures.
- Low grade cytomorphology (lack nuclear pleomorphism).
DDx:
- Choroid plexus papilloma - when infiltrating cerebellopontine angle via petrous bone.
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma.
Images
www:
IHC
- CK7 +ve.
- S-100 +ve (focally).
- CD31 +ve - marks the outline of the papillary structures.[1]
- Kir 7.1-ve - discriminates tumour from plexus papilloma.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Künzel, J.; Agaimy, A.; Hornung, J.; Lell, M.; Ganslandt, O.; Semrau, S.; Zenk, J. (2014). "Sporadic endolymphatic sac tumor--a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7 (5): 2641-6. PMID 24966979. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "pmid24966979" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Friedman, RA.; Hoa, M.; Brackmann, DE. (Feb 2013). "Surgical management of endolymphatic sac tumors.". J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 74 (1): 12-9. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1329622. PMID 24436884.
- ↑ Yang, X.; Liu, XS.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, XH.; Zhang, YK. (2014). "Endolymphatic sac tumor with von Hippel-Lindau disease: report of a case with atypical pathology of endolymphatic sac tumor.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7 (5): 2609-14. PMID 24966975.
- ↑ Schittenhelm, J.; Roser, F.; Tatagiba, M.; Beschorner, R. (Jul 2012). "Diagnostic value of EAAT-1 and Kir7.1 for distinguishing endolymphatic sac tumors from choroid plexus tumors.". Am J Clin Pathol 138 (1): 85-9. doi:10.1309/AJCPPRKNNL09JTLP. PMID 22706862.