Difference between revisions of "Fibrous dysplasia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
*Low grade [[fibrosarcoma]]. | *Low grade [[fibrosarcoma]]. | ||
*[[Low-grade central osteosarcoma]].<ref name=inwards>{{cite journal |author=Inwards, CY |title=Low-grade central osteosarcoma versus fibrous dysplasia |journal=Pathology Case Reviews |volume=6 |issue=1 |pages=22-27 |year=2001 |pmid= |doi= |url= http://journals.lww.com/pathologycasereviews/Fulltext/2001/01000/Low_Grade_Central_Osteosarcoma_Versus_Fibrous.5.aspx }}</ref> | *[[Low-grade central osteosarcoma]].<ref name=inwards>{{cite journal |author=Inwards, CY |title=Low-grade central osteosarcoma versus fibrous dysplasia |journal=Pathology Case Reviews |volume=6 |issue=1 |pages=22-27 |year=2001 |pmid= |doi= |url= http://journals.lww.com/pathologycasereviews/Fulltext/2001/01000/Low_Grade_Central_Osteosarcoma_Versus_Fibrous.5.aspx }}</ref> | ||
*Gnathic ossifying fibroma (Cemento-ossifying fibroma)<ref>http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v20/n3/full/3800753a.html</ref> - Prominent calcified spherules, no associated GNAS mutation | *Gnathic ossifying fibroma (Cemento-ossifying fibroma)<ref>http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v20/n3/full/3800753a.html</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Patel | first1 = MM. | last2 = Wilkey | first2 = JF. | last3 = Abdelsayed | first3 = R. | last4 = D'Silva | first4 = NJ. | last5 = Malchoff | first5 = C. | last6 = Mallya | first6 = SM. | title = Analysis of GNAS mutations in cemento-ossifying fibromas and cemento-osseous dysplasias of the jaws. | journal = Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod | volume = 109 | issue = 5 | pages = 739-43 | month = May | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.12.016 | PMID = 20346714 }}<r/ref> - Prominent calcified spherules, no associated GNAS mutation | ||
** Gnathic ossifying fibroma recurs and needs to be completely enucleated | ** Gnathic ossifying fibroma recurs and needs to be completely enucleated | ||
** Fibrous dysplasia may be self limited and can be followed with observation or if symptomatic bisphosphonate therapy is an option. | ** Fibrous dysplasia may be self limited and can be followed with observation or if symptomatic bisphosphonate therapy is an option. | ||
Revision as of 05:46, 19 October 2014
| Fibrous dysplasia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
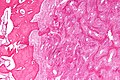
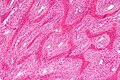
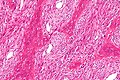
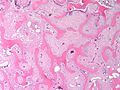
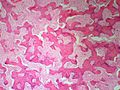
 Fibrous dysplasia. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | osteitis fibrosa |
|
| |
| LM | woven bone with odd irregular shapes (often described as "chinese characters"), fibrous tissue around bone, no osteoblastic rimming |
| LM DDx | desmoplastic fibroma, low-grade fibrosarcoma, low-grade central osteosarcoma |
| Site | bone |
|
| |
| Syndromes | McCune-Albright syndrome |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
Fibrous dysplasia, also osteitis fibrosa, is a rare disorder of bone that has a distinctive microscopic appearance.
General
Classification:
- Monostotic - one bone involved, ~80% of cases.
- Polyostotic - several bones involved, ~20% of cases.
- May be associated with McCune-Albright syndrome.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Woven bone with odd irregular shapes - key feature.
- Described as "chinese characters".[2]
- Fibrous tissue around bone.
Notes:
- No osteoblastic rimming.
DDx:
- Desmoplastic fibroma - has lamellar bone.
- Low grade fibrosarcoma.
- Low-grade central osteosarcoma.[3]
- Gnathic ossifying fibroma (Cemento-ossifying fibroma)[4]<ref>Patel, MM.; Wilkey, JF.; Abdelsayed, R.; D'Silva, NJ.; Malchoff, C.; Mallya, SM. (May 2010). "Analysis of GNAS mutations in cemento-ossifying fibromas and cemento-osseous dysplasias of the jaws.". Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 109 (5): 739-43. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.12.016. PMID 20346714.<r/ref> - Prominent calcified spherules, no associated GNAS mutation
- Gnathic ossifying fibroma recurs and needs to be completely enucleated
- Fibrous dysplasia may be self limited and can be followed with observation or if symptomatic bisphosphonate therapy is an option.
- Distinguishing between these two is important
Images
www:
- Fibrous dysplasia of bone - high mag. (pathologypics.com).
- Fibrous dysplasia of bone - low mag. (pathologypics.com).
- Modern Pathology[1]
See also
- Bone.
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathologypics.com/pictview.aspx?id=104. Accessed on: 14 April 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathcases.com/bone_tumors_and_tumor.htm. Accessed on: 31 May 2011.
- ↑ Inwards, CY (2001). "Low-grade central osteosarcoma versus fibrous dysplasia". Pathology Case Reviews 6 (1): 22-27. http://journals.lww.com/pathologycasereviews/Fulltext/2001/01000/Low_Grade_Central_Osteosarcoma_Versus_Fibrous.5.aspx.
- ↑ http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v20/n3/full/3800753a.html