Difference between revisions of "Eosinophil"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Paneth cells. | *Paneth cells. | ||
**Intraepithelial eosinophils -- have smaller (~1/2) more intensely red granules. | |||
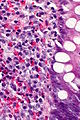
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
Revision as of 00:20, 19 January 2014
Eosinophil is a common type of white blood cell.
General
Disease with many eosinophils
- Infection - esp. fungal.
- Drug reaction.
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp.
- Churg-Strauss syndrome.
- Asthma.
- Kimura disease.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES).[1]
- Eosinophilic myeloproliferative neoplasm.[2]
- Hodgkin lymphoma - eosinophils not malignant.
Site specific
- Eosinophilic esophagitis.
- Eosinophilic colitis.
- Eosinophilic gastritis.
- Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia (ALHE) - skin.
Microscopic
Features:
- Bilobed nucleus.
- Granular eosinophilic cytoplasm.
DDx:
- Paneth cells.
- Intraepithelial eosinophils -- have smaller (~1/2) more intensely red granules.
Images
Eosinophils in eosinophilic colitis. (WC)
See also
References
- ↑ Podjasek, JC.; Butterfield, JH. (Apr 2013). "Mortality in hypereosinophilic syndrome: 19 years of experience at Mayo Clinic with a review of the literature.". Leuk Res 37 (4): 392-5. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2012.12.016. PMID 23332454.
- ↑ Noel, P.; Mesa, RA. (Mar 2013). "Eosinophilic myeloid neoplasms.". Curr Opin Hematol 20 (2): 157-62. doi:10.1097/MOH.0b013e32835d81bf. PMID 23385615.