Difference between revisions of "Whipple's disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| Caption = Whipple's disease. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Whipple's disease. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = | ||
| Micro = | | Micro = rod-shaped microorganisms - typically in macrophages; lamina propria macrophages usually abundant | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[mycobacterium avium complex]] | | LMDDx = [[mycobacterium avium complex]] | ||
Revision as of 03:57, 24 December 2013
| Whipple's disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
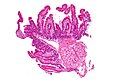
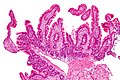
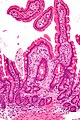
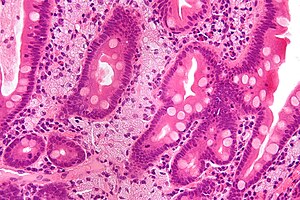 Whipple's disease. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
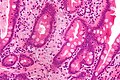
| LM | rod-shaped microorganisms - typically in macrophages; lamina propria macrophages usually abundant |
| LM DDx | mycobacterium avium complex |
| Stains | PAS +ve (microorganisms), AFB -ve |
| Site | duodenum |
|
| |
| Clinical history | usu. middle aged men |
| Signs | diarrhea |
| Prevalence | very rare |
| Prognosis | good |
| Treatment | antibiotics |
Whipple's disease is a rare infectious disease that is classically in the duodenum.
General
Etiology:
Epidemiology:
- Very rare.
- Classically middle aged men.
Clinical
- Malabsorption (diarrhea), arthritis + others.
- Symptoms are non-specific.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics - for months and months.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Infectious microorganism typically found in macrophages.
- Macrophages usually abundant - key feature that should raise Dx in DDx.
- Organisms periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) positive.
DDx:
- Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC).
Images
Stains
Image:
See also
References
- ↑ Liang Z, La Scola B, Raoult D (January 2002). "Monoclonal antibodies to immunodominant epitope of Tropheryma whipplei". Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 9 (1): 156?9. PMC 119894. PMID 11777846. http://cvi.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11777846.
- ↑ Alkan, S.; Beals, TF.; Schnitzer, B. (Dec 2001). "Primary diagnosis of whipple disease manifesting as lymphadenopathy: use of polymerase chain reaction for detection of Tropheryma whippelii.". Am J Clin Pathol 116 (6): 898-904. doi:10.1309/7678-E2DW-HFJ5-QYUJ. PMID 11764080.
- ↑ Bai J, Mazure R, Vazquez H, Niveloni S, Smecuol E, Pedreira S, Mauriño E (2004). "Whipple's disease". Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2 (10): 849?60. doi:10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00387-8. PMID 15476147.