Difference between revisions of "Diverticular disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split-out, +infobox) |
(tweak) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
'''Diverticular disease''', also '''diverticulosis''', is a common disease of the [[colon]]. Inflammation of diverticula is known as '''diverticulitis'''. | '''Diverticular disease''', also '''diverticulosis''', is a common disease of the [[colon]]. Inflammation of diverticula is known as '''diverticulitis'''. | ||
==General== | |||
*Very common. | *Very common. | ||
*Typically seen in elderly patients - 50s and 60s. | |||
Complications: | Complications: | ||
| Line 38: | Line 39: | ||
**Rectal biopsy to differentiate from [[ulcerative colitis]]. | **Rectal biopsy to differentiate from [[ulcerative colitis]]. | ||
==Gross== | |||
*Corrugated - like cardboard. | *Corrugated - like cardboard. | ||
*Wall thickening (reactive).<ref name=pmid21359889>{{Cite journal | last1 = Nicholson | first1 = BD. | last2 = Hyland | first2 = R. | last3 = Rembacken | first3 = BJ. | last4 = Denyer | first4 = M. | last5 = Hull | first5 = MA. | last6 = Tolan | first6 = DJ. | title = Colonoscopy for colonic wall thickening at computed tomography: a worthwhile pursuit? | journal = Surg Endosc | volume = 25 | issue = 8 | pages = 2586-91 | month = Aug | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1007/s00464-011-1591-7 | PMID = 21359889 }}</ref> | *Wall thickening (reactive).<ref name=pmid21359889>{{Cite journal | last1 = Nicholson | first1 = BD. | last2 = Hyland | first2 = R. | last3 = Rembacken | first3 = BJ. | last4 = Denyer | first4 = M. | last5 = Hull | first5 = MA. | last6 = Tolan | first6 = DJ. | title = Colonoscopy for colonic wall thickening at computed tomography: a worthwhile pursuit? | journal = Surg Endosc | volume = 25 | issue = 8 | pages = 2586-91 | month = Aug | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1007/s00464-011-1591-7 | PMID = 21359889 }}</ref> | ||
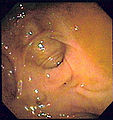
===Endoscopic image=== | |||
<gallery>Image:Diverticulosis_2.jpg | Diverticular disease. (WC/Samir)</gallery> | <gallery>Image:Diverticulosis_2.jpg | Diverticular disease. (WC/Samir)</gallery> | ||
===Grossing notes=== | |||
*[[pp:Diverticular disease]]. | *[[pp:Diverticular disease]]. | ||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Mucosa/submucosa invagination into the musuclaris propria (MP). | *Mucosa/submucosa invagination into the musuclaris propria (MP). | ||
| Line 56: | Line 57: | ||
*[http://histology-group28.wikispaces.com/file/view/divertic.jpg/60992930/divertic.jpg DD (wikispaces.com)].<ref>URL: [http://histology-group28.wikispaces.com/DigestiveSystemProject http://histology-group28.wikispaces.com/DigestiveSystemProject]. Accessed on: 23 August 2011.</ref> | *[http://histology-group28.wikispaces.com/file/view/divertic.jpg/60992930/divertic.jpg DD (wikispaces.com)].<ref>URL: [http://histology-group28.wikispaces.com/DigestiveSystemProject http://histology-group28.wikispaces.com/DigestiveSystemProject]. Accessed on: 23 August 2011.</ref> | ||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
RECTO-SIGMOID, LARGE BOWEL RESECTION: | RECTO-SIGMOID, LARGE BOWEL RESECTION: | ||
| Line 70: | Line 71: | ||
- NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 22:01, 4 August 2013
| Diverticular disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
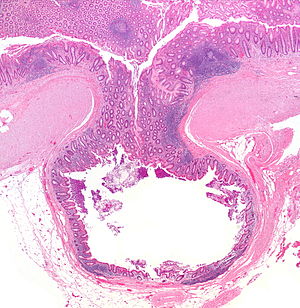 Diverticulum. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | mucosa/submucosa invaginate into the musuclaris propria |
| Site | colon, other sites |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | peritonitis |
| Symptoms | usu. asymptomatic, diverticulitis presents with abdominal pain |
| Clin. DDx | colorectal carcinoma (occasionally) |
Diverticular disease, also diverticulosis, is a common disease of the colon. Inflammation of diverticula is known as diverticulitis.
General
- Very common.
- Typically seen in elderly patients - 50s and 60s.
Complications:
- Diverticulitis.
- Diverticular-associated colitis[1] - rare.
- Rectal biopsy to differentiate from ulcerative colitis.
Gross
- Corrugated - like cardboard.
- Wall thickening (reactive).[2]
Endoscopic image
Grossing notes
Microscopic
Features:
- Mucosa/submucosa invagination into the musuclaris propria (MP).
- At the site the blood vessels supplying the mucosa and submucosa penetrate the MP.[3]
Image:
Sign out
RECTO-SIGMOID, LARGE BOWEL RESECTION: - PERFORATED DIVERTICULITIS WITH SEROSITIS AND ABSCESS FORMATION. - SUBMUCOSAL FIBROSIS. - ONE LYMPH NODE NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY ( 0 POSITIVE / 1 ). - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
SIGMOID COLON, SIGMOIDECTOMY: - DIVERTICULAR DISEASE WITHOUT DIVERTICULITIS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
See also
References
- ↑ Mulhall, AM.; Mahid, SS.; Petras, RE.; Galandiuk, S. (Jun 2009). "Diverticular disease associated with inflammatory bowel disease-like colitis: a systematic review.". Dis Colon Rectum 52 (6): 1072-9. doi:10.1007/DCR.0b013e31819ef79a. PMID 19581849.
- ↑ Nicholson, BD.; Hyland, R.; Rembacken, BJ.; Denyer, M.; Hull, MA.; Tolan, DJ. (Aug 2011). "Colonoscopy for colonic wall thickening at computed tomography: a worthwhile pursuit?". Surg Endosc 25 (8): 2586-91. doi:10.1007/s00464-011-1591-7. PMID 21359889.
- ↑ West, AB.. "The pathology of diverticulitis.". J Clin Gastroenterol 42 (10): 1137-8. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181862a9f. PMID 18936652.
- ↑ URL: http://histology-group28.wikispaces.com/DigestiveSystemProject. Accessed on: 23 August 2011.