Difference between revisions of "Cystic kidney diseases"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→General: wikify) |
(→Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: split out) |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
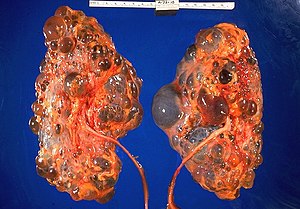
[[Image:Polycystic kidneys, gross pathology 20G0027 lores.jpg|thumb|Polycystic kidneys. (WC/CDC)]] | |||
'''Cystic kidney diseases''', also '''cystic renal diseases''', are a group of [[medical kidney diseases]] characterized by multiple cysts. | '''Cystic kidney diseases''', also '''cystic renal diseases''', are a group of [[medical kidney diseases]] characterized by multiple cysts. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
===Adult=== | ===Adult=== | ||
*Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). | *[[Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease]] (ADPKD). | ||
*Adult-onset medullary cystic disease. | *[[Adult-onset medullary cystic disease]]. | ||
*Acquired renal cystic disease. | *[[Acquired renal cystic disease]]. | ||
*Cystic [[renal cell carcinoma]]. | *Cystic [[renal cell carcinoma]]. | ||
*[[Localized cystic disease of the kidney]]. | |||
===Pediatric=== | ===Pediatric=== | ||
*Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). | *[[Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease]] (ARPKD). | ||
*Medullary sponge kidney. | *Medullary sponge kidney. | ||
*Nephronophthisis. | *Nephronophthisis. | ||
=Specific diseases= | |||
==Benign cortical cyst of the kidney== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''benign cortical cyst''. | |||
{{Main|Benign cortical cyst of the kidney}} | |||
==Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease== | ==Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease== | ||
*Abbreviated ''ADPKD''. | *Abbreviated ''ADPKD''. | ||
{{Main|Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease}} | |||
==Acquired renal cystic disease== | ==Acquired renal cystic disease== | ||
{{Main|Acquired cystic disease of the kidney}} | |||
== | ==Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease== | ||
*Abbreviated ''ARPKD''. | |||
{{Main|Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease}} | |||
==Localized cystic disease of the kidney== | |||
*[[ | *[[AKA]] ''segmental cystic disease of the kidney''. | ||
*[[AKA]] ''unilateral cystic disease of the kidney''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''benign multilocular cyst of the kidney''. | |||
{{Main|Localized cystic disease of the kidney}} | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
*[[Medical kidney diseases]]. | *[[Medical kidney diseases]]. | ||
*[[Kidney tumours]]. | *[[Kidney tumours]]. | ||
*[[Bosniak classification]]. | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
Latest revision as of 14:43, 21 June 2016
Cystic kidney diseases, also cystic renal diseases, are a group of medical kidney diseases characterized by multiple cysts.
Renal neoplasms, e.g. renal cell carcinoma, may be cystic. They are dealt with in kidney tumours.
Overview
Adult
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD).
- Adult-onset medullary cystic disease.
- Acquired renal cystic disease.
- Cystic renal cell carcinoma.
- Localized cystic disease of the kidney.
Pediatric
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD).
- Medullary sponge kidney.
- Nephronophthisis.
Specific diseases
Benign cortical cyst of the kidney
- AKA benign cortical cyst.
Main article: Benign cortical cyst of the kidney
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- Abbreviated ADPKD.
Main article: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Acquired renal cystic disease
Main article: Acquired cystic disease of the kidney
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
- Abbreviated ARPKD.
Main article: Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
Localized cystic disease of the kidney
- AKA segmental cystic disease of the kidney.
- AKA unilateral cystic disease of the kidney.
- AKA benign multilocular cyst of the kidney.
Main article: Localized cystic disease of the kidney