Difference between revisions of "Barrett's esophagus"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→General: ref for goblet cells required) |
(→Gross) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
*Diagnosis is made by '''clinicans ''not'' pathologists'''. | *Diagnosis is made by '''clinicans ''not'' pathologists'''. | ||
**A common histologic correlate is metaplastic transformation of stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells. | **A common histologic correlate is metaplastic transformation of stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells. | ||
***There is disagreement whether goblet cells are required for the diagnosis.<ref name=pmid19623166>{{Cite journal | last1 = Riddell | first1 = RH. | last2 = Odze | first2 = RD. | title = Definition of Barrett's esophagus: time for a rethink--is intestinal metaplasia dead? | journal = Am J Gastroenterol | volume = 104 | issue = 10 | pages = 2588-94 | month = Oct | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1038/ajg.2009.390 | PMID = 19623166 }}</ref> In the United States and Canada goblet cells are required for the diagnosis.<ref name=pmid29998421>{{cite journal | | ***There is disagreement whether goblet cells are required for the diagnosis.<ref name=pmid19623166>{{Cite journal | last1 = Riddell | first1 = RH. | last2 = Odze | first2 = RD. | title = Definition of Barrett's esophagus: time for a rethink--is intestinal metaplasia dead? | journal = Am J Gastroenterol | volume = 104 | issue = 10 | pages = 2588-94 | month = Oct | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1038/ajg.2009.390 | PMID = 19623166 }}</ref> In the United States and Canada goblet cells are required for the diagnosis.<ref name=pmid29998421>{{cite journal |authors=Odze R |title=Histology of Barrett's Metaplasia: Do Goblet Cells Matter? |journal=Dig. Dis. Sci. |volume=63 |issue=8 |pages=2042–2051 |date=August 2018 |pmid=29998421 |doi=10.1007/s10620-018-5151-z |url=}}</ref> In the UK, goblet cells are not required. | ||
****One large study suggests that goblets cells are only absent due to undersampling.<ref name=pmid21959311>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chandrasoma | first1 = P. | last2 = Wijetunge | first2 = S. | last3 = DeMeester | first3 = S. | last4 = Ma | first4 = Y. | last5 = Hagen | first5 = J. | last6 = Zamis | first6 = L. | last7 = DeMeester | first7 = T. | title = Columnar-lined esophagus without intestinal metaplasia has no proven risk of adenocarcinoma. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 36 | issue = 1 | pages = 1-7 | month = Jan | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822a5a2c | PMID = 21959311 }}</ref> | ****One large study suggests that goblets cells are only absent due to undersampling.<ref name=pmid21959311>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chandrasoma | first1 = P. | last2 = Wijetunge | first2 = S. | last3 = DeMeester | first3 = S. | last4 = Ma | first4 = Y. | last5 = Hagen | first5 = J. | last6 = Zamis | first6 = L. | last7 = DeMeester | first7 = T. | title = Columnar-lined esophagus without intestinal metaplasia has no proven risk of adenocarcinoma. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 36 | issue = 1 | pages = 1-7 | month = Jan | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822a5a2c | PMID = 21959311 }}</ref> | ||
*Associated with [[gastroesophageal reflux disease]] (GERD). | *Associated with [[gastroesophageal reflux disease]] (GERD). | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
**Normal mucosa = light pink. | **Normal mucosa = light pink. | ||
===Prague Classification Barrett's Esophagus=== | |||
*Commonly used in by endoscopists. | |||
*Quantifies the extent of Barrett's esophagus. | |||
Meaning:<ref name=pmid22248595>{{cite journal |vauthors=Vahabzadeh B, Seetharam AB, Cook MB, Wani S, Rastogi A, Bansal A, Early DS, Sharma P |title=Validation of the Prague C & M criteria for the endoscopic grading of Barrett's esophagus by gastroenterology trainees: a multicenter study |journal=Gastrointest Endosc |volume=75 |issue=2 |pages=236–41 |date=February 2012 |pmid=22248595 |pmc=4547779 |doi=10.1016/j.gie.2011.09.017 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*C = circumferential length. | |||
*M = maximal length. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
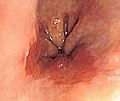
Image:Barretts_esophagus.jpg | Endoscopic image of BE. (WC) | Image:Barretts_esophagus.jpg | Endoscopic image of BE. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
Latest revision as of 14:23, 15 September 2022
| Barrett's esophagus | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
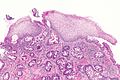
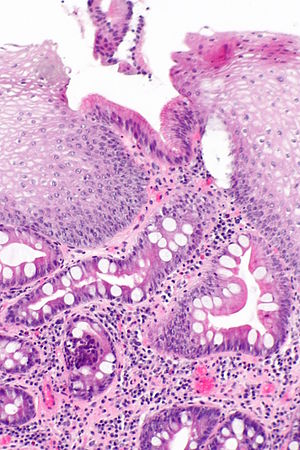 Esophagus with intestinal metaplasia, as seen in Barrett esophagus. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | columnar epithelium with goblet cells |
| LM DDx | low-grade columnar dysplasia of the esophagus, gastroesophageal reflux disease, nonspecific inflammation at the GE junction |
| Stains | Alcian blue stain (pH 2.5) |
| Site | esophagus |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | gastroesophageal reflux disease, esophageal adenocarcinoma, columnar dysplasia of the esophagus |
| Prevalence | relatively common |
| Endoscopy | red/light brown esophageal mucosa, at gastro-esophageal junction |
| Prognosis | good |
| Treatment | on-going surveillance for columnar dysplasia |
- Intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus redirects here.
Barrett's esophagus, abbreviated BE, is a relatively common pathology of the esophagus, that is associated with an increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
General
- Diagnosis is made by clinicans not pathologists.
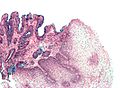
- A common histologic correlate is metaplastic transformation of stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells.
- Associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Considered to be a consequence of chronic GERD.[4]
Significance of Barrett's esophagus:
- Increased risk of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.
- Need on-going surveillance, i.e. long term follow-up/repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Gross
- Red/light brown esophageal mucosa.
- Normal mucosa = light pink.
Prague Classification Barrett's Esophagus
- Commonly used in by endoscopists.
- Quantifies the extent of Barrett's esophagus.
Meaning:[5]
- C = circumferential length.
- M = maximal length.
Images
Microscopic
Features:
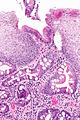
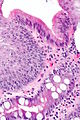
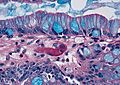
- Columnar epithelium with:
- Goblet cells - key feature.
- +/-Moderate chronic inflammation +/- acute inflammation -- common.[6]
- +/-Mild nuclear hyperchromasia.
- +/-Squamous epithelium with changes of gastroesophageal reflux.
DDx:
- Chronic gastritis.
- Helicobacter gastritis.
- Low-grade columnar dysplasia of the esophagus.
- Carry over from a concurrent duodenal biopsy - fragments with goblets cells have no gastric-type epithelium.
Images
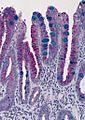
Barrett's type mucosa. Alcian blue stain. (WC)
Stains
- Alcian blue (pH 2.5)[7] - goblet cells +ve.
Sign-out
Esophagus, Distal, Biopsy: - Columnar epithelium with intestinal metaplasia, see comment. - Reactive squamous epithelium. - NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy. Comment: The findings are consistent with Barrett's esophagus in the appropriate endoscopic setting.
Block letters
ESOPHAGUS, DISTAL, BIOPSY: - COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM WITH INTESTINAL METAPLASIA AND MILD ACUTE INFLAMMATION, SEE COMMENT. - REACTIVE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: The findings are consistent with Barrett's esophagus in the appropriate endoscopic setting.
ESOPHAGUS, DISTAL, BIOPSY: - COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM WITH INTESTINAL METAPLASIA AND MODERATE CHRONIC INFLAMMATION, SEE COMMENT. - REACTIVE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: The findings are consistent with Barrett's esophagus in the appropriate endoscopic setting.
ESOPHAGUS, DISTAL, BIOPSY: - COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM WITH EXTENSIVE INTESTINAL METAPLASIA, ACUTE AND CHRONIC INFLAMMATION; - SEE COMMENT. - REACTIVE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: The columnar epithelium with intestinal metplasia is seen located deep to the squamous epithelium. The findings are consistent with Barrett's esophagus in the appropriate endoscopic setting.
See also
References
- ↑ Riddell, RH.; Odze, RD. (Oct 2009). "Definition of Barrett's esophagus: time for a rethink--is intestinal metaplasia dead?". Am J Gastroenterol 104 (10): 2588-94. doi:10.1038/ajg.2009.390. PMID 19623166.
- ↑ Odze R (August 2018). "Histology of Barrett's Metaplasia: Do Goblet Cells Matter?". Dig. Dis. Sci. 63 (8): 2042–2051. doi:10.1007/s10620-018-5151-z. PMID 29998421.
- ↑ Chandrasoma, P.; Wijetunge, S.; DeMeester, S.; Ma, Y.; Hagen, J.; Zamis, L.; DeMeester, T. (Jan 2012). "Columnar-lined esophagus without intestinal metaplasia has no proven risk of adenocarcinoma.". Am J Surg Pathol 36 (1): 1-7. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822a5a2c. PMID 21959311.
- ↑ Yantiss, RK. (Nov 2010). "Diagnostic challenges in the pathologic evaluation of Barrett esophagus.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 134 (11): 1589-600. doi:10.1043/2009-0547-RAR1.1. PMID 21043812.
- ↑ "Validation of the Prague C & M criteria for the endoscopic grading of Barrett's esophagus by gastroenterology trainees: a multicenter study". Gastrointest Endosc 75 (2): 236–41. February 2012. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.09.017. PMC 4547779. PMID 22248595. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4547779/.
- ↑ Voutilainen, M.; Färkkilä, M.; Mecklin, JP.; Juhola, M.; Sipponen, P. (Nov 1999). "Chronic inflammation at the gastroesophageal junction (carditis) appears to be a specific finding related to Helicobacter pylori infection and gastroesophageal reflux disease. The Central Finland Endoscopy Study Group.". Am J Gastroenterol 94 (11): 3175-80. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01513.x. PMID 10566710.
- ↑ Voutilainen, M.; Färkkilä, M.; Juhola, M.; Mecklin, JP.; Sipponen, P. (Nov 1999). "Complete and incomplete intestinal metaplasia at the oesophagogastric junction: prevalences and associations with endoscopic erosive oesophagitis and gastritis.". Gut 45 (5): 644-8. PMID 10517897.