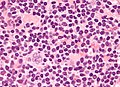
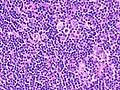
Difference between revisions of "Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (add image) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
|CD57 || rosettes around malign. cells || - | |CD57 || rosettes around malign. cells || - | ||
|- | |- | ||
|EBER | |[[EBER]] || -ve || +ve/-ve | ||
|- | |- | ||
|EMA || +ve/-ve || -ve | |EMA || +ve/-ve || -ve | ||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Popcorn_cell_in_nodular_lymphocyte_predominant_Hodgkin_lymphoma_-_very_high_mag_cropped.jpg | Popcorn cell. (WC) | Image:Popcorn_cell_in_nodular_lymphocyte_predominant_Hodgkin_lymphoma_-_very_high_mag_cropped.jpg | Popcorn cell. (WC) | ||
Image:Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma.jpg | LP/popcorn cells (WC) | Image:Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma.jpg | LP/popcorn cells (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==See also== | |||
*[[Hematopathology]]. | |||
*[[Hodgkin lymphoma]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Haematopathology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:04, 26 December 2019
| Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
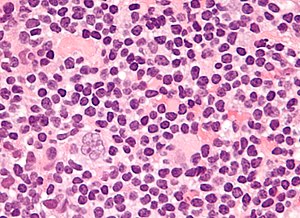 Popcorn cell in nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma | |
|
| |
| LM | Popcorn cells (relatively) small (compared to classic RSCs) - have lobulated nucleus (key feature), small nucleoli; subtle nodularity at low power |
| Subtypes | none |
| LM DDx |
diffuse large B cell lymphoma (esp. T-cell/histiocytic-rich LBCL), anaplastic large cell lymphoma, B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma, classical Hodgkin lymphoma |
| IHC | LCA (CD45) +ve, CD20 +ve, CD10 +ve, Bcl-6 +ve, EMA +ve, CD30 -ve, CD15 -ve |
| Site | usu. lymph node |
|
| |
| Signs | lymphadenopathy |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | good |
- AKA lympho-histiocytic variant.
- Abbreviated NLPHL.
- Different IHC and morphologic appearance than classic HL.
- Significant risk for transformation into diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL); 10-year cumulative transformation rate (to DLBCL) in one study was 12%.[1]
Microscopy
Features (nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma):
- Popcorn cell (previously known as Lymphocytic & histiocytic cell (L&H cell)[2]) - variant of RSC:
- Cells (relatively) small (compared to classic RSCs).
- Lobulated nucleus - key feature.
- Small nucleoli.
- Subtle nodularity at low power (2.5x or 5x objective).
IHC
Abbreviated panel:[3]
- CD30 Reed-Sternberg cells (RSCs) +ve ~98%
- CD15 Reed-Sternberg cells +ve ~80%, stains neutrophils.
- CD45 often negative in RSCs.
- CD20 may stain RSCs.
- PAX5 +ve.[4]
Additional - for completeness:
- CD3 (T lymphocytes)
NLPHL IHC differs from the classical HL:[4]
- LCA +ve.
- CD20 +ve.
- CD10 +ve.
- Bcl-6 +ve.
- EMA +ve.
- CD30 -ve
- CD15 -ve.
A panel
| Antibody | NLPHL | CHL |
| CD45 | +ve | -ve |
| CD20 | +ve | -ve |
| BCL6 | ||
| MUM1[5] | -ve | |
| CD30 | -ve | +ve (most sensitive). |
| CD15 | -ve | +ve |
| CD21 | networks present | no networks |
| CD23 | networks present | no networks |
| OCT-2 | +ve | -ve |
| PAX5 | +ve | +ve (proves B cell linage) |
| CD3 | usu. < benign B cell | usu. > benign B cell component |
| CD57 | rosettes around malign. cells | - |
| EBER | -ve | +ve/-ve |
| EMA | +ve/-ve | -ve |
| 4 unstained |
Images (NLPHL)
www:
See also
References
- ↑ Biasoli I, Stamatoullas A, Meignin V, et al. (February 2010). "Nodular, lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: a long-term study and analysis of transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in a cohort of 164 patients from the Adult Lymphoma Study Group". Cancer 116 (3): 631–9. doi:10.1002/cncr.24819. PMID 20029973.
- ↑ Küppers R, Rajewsky K, Braeuninger A, Hansmann ML (March 1998). "L&H cells in lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's disease". N. Engl. J. Med. 338 (11): 763–4; author reply 764–5. doi:10.1056/NEJM199803123381113. PMID 9499174.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 568. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 683. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/601900. Accessed on: 10 August 2010.