Difference between revisions of "Cutaneous calcinosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Micro) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Cutaneous calcinosis. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Cutaneous calcinosis. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = cutaneous calcification | | Synonyms = cutaneous calcification, calcinosis cutis | ||
| Micro = dermal calcification - usu. well-circumscribed | | Micro = dermal calcification - usu. well-circumscribed | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| Tx = excision | | Tx = excision | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Cutaneous calcinosis''', also '''calcinosis cutis''', is calcification of the [[skin]]. It is benign in itself; however, the underlying cause not be. | '''Cutaneous calcinosis''', also '''calcinosis cutis''' and '''cutaneous calcification''', is calcification of the [[skin]]. It is benign in itself; however, the underlying cause may ''not'' be. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
===Micro=== | ===Micro=== | ||
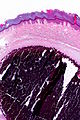
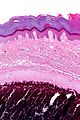
The sections show | The sections show calcifications surrounded by macrophages and giant cells. No nuclear atypia is apparent. The overlying epidermis is unremarkable. | ||
====Without epidermis==== | |||
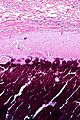
The sections show dermal/subcutaneous calcifications surrounded by fibrosis, macrophages and giant cells. No nuclear atypia is apparent. Overlying epidermis is absent. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Non-malignant skin disease]]. | *[[Non-malignant skin disease]]. | ||
*[[Heterotopic ossification]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:24, 22 February 2017
| Cutaneous calcinosis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
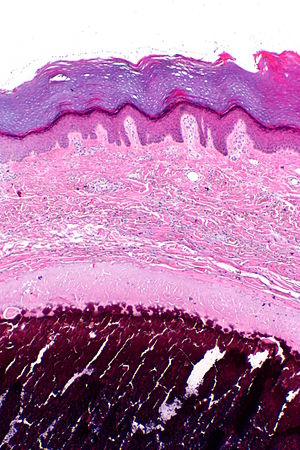 Cutaneous calcinosis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | cutaneous calcification, calcinosis cutis |
|
| |
| LM | dermal calcification - usu. well-circumscribed |
| Gross | firm nodule |
| Site | skin, scrotum |
|
| |
| Clinical history | +/-trauma at the site |
| Signs | firm nodule |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | excision |
Cutaneous calcinosis, also calcinosis cutis and cutaneous calcification, is calcification of the skin. It is benign in itself; however, the underlying cause may not be.
General
- Benign in itself; underlying cause may not be benign.
- May be a scrotal lesion - known as scrotal calcinosis.[1]
Subtypes:[2]
- Dystrophic - due to death of cells; may be related to a tumour.
- Metastatic - due to chronic renal failure; hyperkalemia; paraneoplastic phenomenon.
- Iatrogenic - post surgical.
- Idiopathic.
Gross
- Firm nodule.
Microscopic
Features:
- Dermal calcification:
- Acellular purple blobs on H&E.
- +/-Artefactual tearing of surrounding tissue due to processing (cutting).
- +/-Small artefactual lines ~1-2 micrometers due to processing (cutting).
- +/-Greyish rim of paucicellular material.
- Usu. well-circumscribed.
- May be surrounded by a palisading granuloma & giant cells.
- Acellular purple blobs on H&E.
Images
www:
Sign out
SKIN AND SUBCUTANEOUS LESION, LEFT HIP, EXCISION: - SUBCUTANEOUS CALCIFICATION SURROUNDED BY BENIGN FIBROUS TISSUE. - DERMAL SCAR. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
SUBCUTANEOUS MASS, OVER BURSA OF ELBOW, EXCISION: - CALCINOSIS CUTIS.
Micro
The sections show calcifications surrounded by macrophages and giant cells. No nuclear atypia is apparent. The overlying epidermis is unremarkable.
Without epidermis
The sections show dermal/subcutaneous calcifications surrounded by fibrosis, macrophages and giant cells. No nuclear atypia is apparent. Overlying epidermis is absent.
See also
References
- ↑ Dubey, S.; Sharma, R.; Maheshwari, V. (2010). "Scrotal calcinosis: idiopathic or dystrophic?". Dermatol Online J 16 (2): 5. PMID 20178701.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1103137-overview. Accessed on: 21 September 2011.