Difference between revisions of "Anaplastic large cell lymphoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images: +image) |
m (additional features) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
ALK IHC - systemic form: | ALK IHC - systemic form: | ||
* +ve = good prognosis | * +ve = good prognosis (generally a disease of children, teenagers and young adults) | ||
* -ve = bad prognosis | * -ve = bad prognosis | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
*Usually appear cohesive. | *Usually appear cohesive. | ||
*May be subcapsular in a [[lymph node]] and mimic a carcinoma. | *May be subcapsular in a [[lymph node]] and mimic a carcinoma. | ||
*''Hallmark cells'' = "horseshoe-shaped or donut-shaped nucleus + eosinophilic paranuclear region"<ref name=pmid17941004>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rapkiewicz | first1 = A. | last2 = Wen | first2 = H. | last3 = Sen | first3 = F. | last4 = Das | first4 = K. | title = Cytomorphologic examination of anaplastic large cell lymphoma by fine-needle aspiration cytology. | journal = Cancer | volume = 111 | issue = 6 | pages = 499-507 | month = Dec | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1002/cncr.23120 | PMID = 17941004 | url=http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.23120/full}}</ref><ref name=pmid12419758>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ponzoni | first1 = M. | last2 = Terreni | first2 = MR. | last3 = Ciceri | first3 = F. | last4 = Ferreri | first4 = AJ. | last5 = Gerevini | first5 = S. | last6 = Anzalone | first6 = N. | last7 = Valle | first7 = M. | last8 = Pizzolito | first8 = S. | last9 = Arrigoni | first9 = G. | title = Primary brain CD30+ ALK1+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma ('ALKoma'): the first case with a combination of 'not common' variants. | journal = Ann Oncol | volume = 13 | issue = 11 | pages = 1827-32 | month = Nov | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12419758 }}</ref> - '''key feature'''. | *''Hallmark cells'' = "horseshoe-shaped or [[donut cell|donut-shaped nucleus]] + eosinophilic paranuclear region"<ref name=pmid17941004>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rapkiewicz | first1 = A. | last2 = Wen | first2 = H. | last3 = Sen | first3 = F. | last4 = Das | first4 = K. | title = Cytomorphologic examination of anaplastic large cell lymphoma by fine-needle aspiration cytology. | journal = Cancer | volume = 111 | issue = 6 | pages = 499-507 | month = Dec | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1002/cncr.23120 | PMID = 17941004 | url=http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.23120/full}}</ref><ref name=pmid12419758>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ponzoni | first1 = M. | last2 = Terreni | first2 = MR. | last3 = Ciceri | first3 = F. | last4 = Ferreri | first4 = AJ. | last5 = Gerevini | first5 = S. | last6 = Anzalone | first6 = N. | last7 = Valle | first7 = M. | last8 = Pizzolito | first8 = S. | last9 = Arrigoni | first9 = G. | title = Primary brain CD30+ ALK1+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma ('ALKoma'): the first case with a combination of 'not common' variants. | journal = Ann Oncol | volume = 13 | issue = 11 | pages = 1827-32 | month = Nov | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12419758 }}</ref> - '''key feature'''. | ||
**The donut-shaped version is also known as a "wreath cell"<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Amin | first1 = HM. | last2 = Lai | first2 = R. | title = Pathobiology of ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. | journal = Blood | volume = 110 | issue = 7 | pages = 2259-67 | month = Oct | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1182/blood-2007-04-060715 | PMID = 17519389 | url=http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/content/110/7/2259.full.html}}</ref> - large (multi-nucleated) cells with (morphologically) one toroidal-shaped nucleus. | **The donut-shaped version is also known as a "wreath cell"<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Amin | first1 = HM. | last2 = Lai | first2 = R. | title = Pathobiology of ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. | journal = Blood | volume = 110 | issue = 7 | pages = 2259-67 | month = Oct | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1182/blood-2007-04-060715 | PMID = 17519389 | url=http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/content/110/7/2259.full.html}}</ref> - large (multi-nucleated) cells with (morphologically) one toroidal-shaped nucleus. | ||
*ALK+ ALCL includes variants without the classical hallmark cells, e.g. small cell variant and lymphohistiocytic variant | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Hodgkin's lymphoma]]. | *[[Hodgkin's lymphoma]] | ||
*Carcinoma | *Anaplastic variants of other haematolymphoid malignancies, e.g. DLBCL or myeloma | ||
*Carcinoma | |||
*Melanoma | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 70: | Line 73: | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*CD30 +ve | *CD30 +ve (usually strong and diffuse) | ||
*ALK-1 -ve/+ve; strongly supports ALCL Dx if +ve. | *ALK-1 -ve/+ve; strongly supports ALCL Dx if +ve. | ||
*CD45 +ve. | *CD45 +ve. | ||
| Line 77: | Line 80: | ||
*CD7 -ve/+ve. | *CD7 -ve/+ve. | ||
*EMA +ve. | *EMA +ve. | ||
*Cytotoxic markers (e.g. TIA, perforin) | |||
==Molecular== | ==Molecular== | ||
*t(2,5)(p23;q35)<ref name=pmid8547653>{{cite journal |author=Lamant L, Meggetto F, al Saati T, ''et al.'' |title=High incidence of the t(2;5)(p23;q35) translocation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and its lack of detection in Hodgkin's disease. Comparison of cytogenetic analysis, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, and P-80 immunostaining |journal=Blood |volume=87 |issue=1 |pages=284–91 |year=1996 |month=January |pmid=8547653 |doi= |url=}}</ref> - | *In ALK+ ALCL, there is commonly an ALK1 rearrangement. | ||
**This may be ALK::NPM1, i.e. t(2,5)(p23;q35)<ref name=pmid8547653>{{cite journal |author=Lamant L, Meggetto F, al Saati T, ''et al.'' |title=High incidence of the t(2;5)(p23;q35) translocation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and its lack of detection in Hodgkin's disease. Comparison of cytogenetic analysis, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, and P-80 immunostaining |journal=Blood |volume=87 |issue=1 |pages=284–91 |year=1996 |month=January |pmid=8547653 |doi= |url=}}</ref> - combined nuclear and cytoplasmic ALK staining is a surrogate for this translocation. | |||
*Other non-NPM1 partners may occur. A ALK1 break-apart probe will detect these. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:00, 29 September 2023
| Anaplastic large cell lymphoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
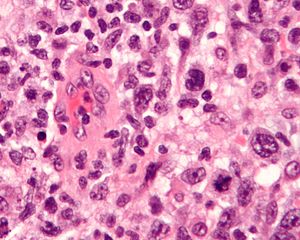 Anaplastic large cell lymphoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | large cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm, Hallmark cells ("horseshoe-shaped or donut-shaped nucleus + eosinophilic paranuclear region") |
| LM DDx | Hodgkin's lymphoma, poorly differentiated carcinoma |
| IHC | CD30 +ve, ALK-1 -ve/+ve, CD45 +ve, CD4 +ve, CD3 -ve/+ve, CD7 -ve/+ve, EMA +ve |
| Molecular | t(2,5)(p23;q35) |
| Site | skin, lymph node, other |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | good to poor, dependent on ALK status and site |
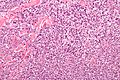
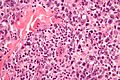
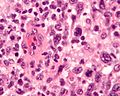
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, abbreviated ALCL, is an uncommon large cell lymphoma.
General
- May look a lot like a carcinoma.
- Often subcapsular in LNs.
- Usually T-cell derived.
- May be isolated to the skin - good prognosis.
Subtypes:
- Systemic ALCL.
- Cutaneous ALCL -- ALK -ve.
ALK IHC - systemic form:
- +ve = good prognosis (generally a disease of children, teenagers and young adults)
- -ve = bad prognosis
Microscopic
Features:
- Large cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Usually appear cohesive.
- May be subcapsular in a lymph node and mimic a carcinoma.
- Hallmark cells = "horseshoe-shaped or donut-shaped nucleus + eosinophilic paranuclear region"[1][2] - key feature.
- The donut-shaped version is also known as a "wreath cell"[3] - large (multi-nucleated) cells with (morphologically) one toroidal-shaped nucleus.
- ALK+ ALCL includes variants without the classical hallmark cells, e.g. small cell variant and lymphohistiocytic variant
DDx:
- Hodgkin's lymphoma
- Anaplastic variants of other haematolymphoid malignancies, e.g. DLBCL or myeloma
- Carcinoma
- Melanoma
Images
www:
IHC
Features:
- CD30 +ve (usually strong and diffuse)
- ALK-1 -ve/+ve; strongly supports ALCL Dx if +ve.
- CD45 +ve.
- CD4 +ve.
- CD3 -ve/+ve.
- CD7 -ve/+ve.
- EMA +ve.
- Cytotoxic markers (e.g. TIA, perforin)
Molecular
- In ALK+ ALCL, there is commonly an ALK1 rearrangement.
- This may be ALK::NPM1, i.e. t(2,5)(p23;q35)[4] - combined nuclear and cytoplasmic ALK staining is a surrogate for this translocation.
- Other non-NPM1 partners may occur. A ALK1 break-apart probe will detect these.
See also
References
- ↑ Rapkiewicz, A.; Wen, H.; Sen, F.; Das, K. (Dec 2007). "Cytomorphologic examination of anaplastic large cell lymphoma by fine-needle aspiration cytology.". Cancer 111 (6): 499-507. doi:10.1002/cncr.23120. PMID 17941004. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.23120/full.
- ↑ Ponzoni, M.; Terreni, MR.; Ciceri, F.; Ferreri, AJ.; Gerevini, S.; Anzalone, N.; Valle, M.; Pizzolito, S. et al. (Nov 2002). "Primary brain CD30+ ALK1+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma ('ALKoma'): the first case with a combination of 'not common' variants.". Ann Oncol 13 (11): 1827-32. PMID 12419758.
- ↑ Amin, HM.; Lai, R. (Oct 2007). "Pathobiology of ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma.". Blood 110 (7): 2259-67. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-04-060715. PMID 17519389. http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/content/110/7/2259.full.html.
- ↑ Lamant L, Meggetto F, al Saati T, et al. (January 1996). "High incidence of the t(2;5)(p23;q35) translocation in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and its lack of detection in Hodgkin's disease. Comparison of cytogenetic analysis, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, and P-80 immunostaining". Blood 87 (1): 284–91. PMID 8547653.