Difference between revisions of "Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (touch) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Nasopharyngeal_angiofibroma_-_2_-_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = fibroblastic cells with plump (near cuboidal) nuclei, fibrous stroma, abundant capillaries | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[head and neck pathology|head and neck]] - nasopharynx | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = male, adolescents young to adults, frequent nose bleeds | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = surgical resection | |||
}} | |||
'''Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma''' is a benign lesion of the [[head and neck pathology|head and neck]]. | '''Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma''' is a benign lesion of the [[head and neck pathology|head and neck]]. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 36: | ||
**Age range 8-41 in one series of 162 cases.<ref name=pmid24222212>{{Cite journal | last1 = Huang | first1 = Y. | last2 = Liu | first2 = Z. | last3 = Wang | first3 = J. | last4 = Sun | first4 = X. | last5 = Yang | first5 = L. | last6 = Wang | first6 = D. | title = Surgical management of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: analysis of 162 cases from 1995 to 2012. | journal = Laryngoscope | volume = 124 | issue = 8 | pages = 1942-6 | month = Aug | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1002/lary.24522 | PMID = 24222212 }} | **Age range 8-41 in one series of 162 cases.<ref name=pmid24222212>{{Cite journal | last1 = Huang | first1 = Y. | last2 = Liu | first2 = Z. | last3 = Wang | first3 = J. | last4 = Sun | first4 = X. | last5 = Yang | first5 = L. | last6 = Wang | first6 = D. | title = Surgical management of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: analysis of 162 cases from 1995 to 2012. | journal = Laryngoscope | volume = 124 | issue = 8 | pages = 1942-6 | month = Aug | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1002/lary.24522 | PMID = 24222212 }} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
*Can be subtyped by location into three groups.<ref name=pmid23332298>{{Cite journal | last1 = Yi | first1 = Z. | last2 = Fang | first2 = Z. | last3 = Lin | first3 = G. | last4 = Lin | first4 = C. | last5 = Xiao | first5 = W. | last6 = Li | first6 = Z. | last7 = Cheng | first7 = J. | last8 = Zhou | first8 = A. | title = Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: a concise classification system and appropriate treatment options. | journal = Am J Otolaryngol | volume = 34 | issue = 2 | pages = 133-41 | month = | year = | doi = 10.1016/j.amjoto.2012.10.004 | PMID = 23332298 }}</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 14: | Line 46: | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
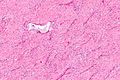
Image: | Image: Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma - intermed mag.jpg | Intermed. mag. | ||
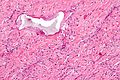
Image: | Image: Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma - high mag.jpg | High mag. | ||
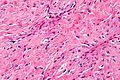
Image: Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma - very high mag.jpg | Very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | |||
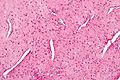
Image: Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma - 2 - high mag.jpg | High mag. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 06:25, 14 January 2015
| Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
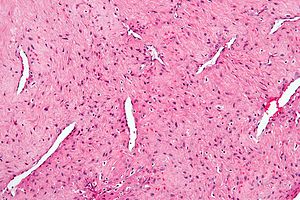 Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | fibroblastic cells with plump (near cuboidal) nuclei, fibrous stroma, abundant capillaries |
| Site | head and neck - nasopharynx |
|
| |
| Clinical history | male, adolescents young to adults, frequent nose bleeds |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | surgical resection |
Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma is a benign lesion of the head and neck.
General
- Classically adolescent males with recurrent nose bleeds.
- Age range 8-41 in one series of 162 cases.[1]
- Can be subtyped by location into three groups.[2]
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Fibroblastic cells with plump (near cuboidal) nuclei.
- Fibrous stroma.
- Abundant capillaries.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, D. (Aug 2014). "Surgical management of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: analysis of 162 cases from 1995 to 2012.". Laryngoscope 124 (8): 1942-6. doi:10.1002/lary.24522. PMID 24222212.
- ↑ Yi, Z.; Fang, Z.; Lin, G.; Lin, C.; Xiao, W.; Li, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, A.. "Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: a concise classification system and appropriate treatment options.". Am J Otolaryngol 34 (2): 133-41. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2012.10.004. PMID 23332298.
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 144. ISBN 978-1416002741.