Difference between revisions of "Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Microscopic) |
(add main subtypes) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
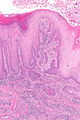
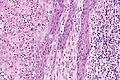
| Image = | | Image = Squamous carcinoma of the penis -- low mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = | | Caption = Squamous carcinoma of the penis. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = | ||
| Micro = | | Micro = | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = HPV-related SCC, Non-HPV-related SCC | ||
| LMDDx = | | LMDDx = [[penile intraepithelial neoplasia]], [[pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = | | IHC = | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| IF = | | IF = | ||
| Gross = mass lesion, scaly patches/nodules, usu. erythematous, +/-ulceration. | | Gross = mass lesion, scaly patches/nodules, usu. erythematous, +/-ulceration. | ||
| Grossing = | | Grossing = [[penectomy]] | ||
| Site = [[penis]] | | Site = [[penis]] | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis''' is the most common malignancy of the [[penis]]. | '''Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis''' is the most common malignancy of the [[penis]]. | ||
''Penile cancer'' redirects to this article. | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Not very common overall.<ref name=pmid24119832>{{Cite journal | last1 = Burt | first1 = LM. | last2 = Shrieve | first2 = DC. | last3 = Tward | first3 = JD. | title = Stage presentation, care patterns, and treatment outcomes for squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. | journal = Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys | volume = 88 | issue = 1 | pages = 94-100 | month = Jan | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.08.013 | PMID = 24119832 }}</ref> | *Not very common overall.<ref name=pmid24119832>{{Cite journal | last1 = Burt | first1 = LM. | last2 = Shrieve | first2 = DC. | last3 = Tward | first3 = JD. | title = Stage presentation, care patterns, and treatment outcomes for squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. | journal = Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys | volume = 88 | issue = 1 | pages = 94-100 | month = Jan | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.08.013 | PMID = 24119832 }}</ref> | ||
*Most common form of | *Most common form of penile cancer. | ||
**Non-squamous penis cancer only ~5% of cases.<ref name=pmid24292119>{{Cite journal | last1 = Moses | first1 = KA. | last2 = Sfakianos | first2 = JP. | last3 = Winer | first3 = A. | last4 = Bernstein | first4 = M. | last5 = Russo | first5 = P. | last6 = Dalbagni | first6 = G. | title = Non-squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: single-center, 15-year experience. | journal = World J Urol | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Dec | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1007/s00345-013-1216-y | PMID = 24292119 }}</ref> | **Non-squamous penis cancer only ~5% of cases.<ref name=pmid24292119>{{Cite journal | last1 = Moses | first1 = KA. | last2 = Sfakianos | first2 = JP. | last3 = Winer | first3 = A. | last4 = Bernstein | first4 = M. | last5 = Russo | first5 = P. | last6 = Dalbagni | first6 = G. | title = Non-squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: single-center, 15-year experience. | journal = World J Urol | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Dec | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1007/s00345-013-1216-y | PMID = 24292119 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 42: | ||
*Median age ~ 67 years old. | *Median age ~ 67 years old. | ||
*Usually a good outcome - 5 year cause specific survival ~ 81%.<ref name=pmid24119832/> | *Usually a good outcome - 5 year cause specific survival ~ 81%.<ref name=pmid24119832/> | ||
*Possible association with sex with animals.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zequi | first1 = Sde C. | last2 = Guimarães | first2 = GC. | last3 = da Fonseca | first3 = FP. | last4 = Ferreira | first4 = U. | last5 = de Matheus | first5 = WE. | last6 = Reis | first6 = LO. | last7 = Aita | first7 = GA. | last8 = Glina | first8 = S. | last9 = Fanni | first9 = VS. | title = Sex with animals (SWA): behavioral characteristics and possible association with penile cancer. A multicenter study. | journal = J Sex Med | volume = 9 | issue = 7 | pages = 1860-7 | month = Jul | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02512.x | PMID = 22023719 }}</ref> | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
*Scaly patches/nodules. | *Scaly patches/nodules. | ||
* | *Usually erythematous. | ||
*+/-Ulceration. | *+/-Ulceration. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 54: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*[[Lymphovascular invasion]] - prognostically important,<ref name=pmid19488760>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bhagat | first1 = SK. | last2 = Gopalakrishnan | first2 = G. | last3 = Kekre | first3 = NS. | last4 = Chacko | first4 = NK. | last5 = Kumar | first5 = S. | last6 = Manipadam | first6 = MT. | last7 = Samuel | first7 = P. | title = Factors predicting inguinal node metastasis in squamous cell cancer of penis. | journal = World J Urol | volume = 28 | issue = 1 | pages = 93-8 | month = Feb | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s00345-009-0421-1 | PMID = 19488760 }}</ref> and changes the T-stage for pT1a tumours to pT1b. | *[[Lymphovascular invasion]] - prognostically important,<ref name=pmid19488760>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bhagat | first1 = SK. | last2 = Gopalakrishnan | first2 = G. | last3 = Kekre | first3 = NS. | last4 = Chacko | first4 = NK. | last5 = Kumar | first5 = S. | last6 = Manipadam | first6 = MT. | last7 = Samuel | first7 = P. | title = Factors predicting inguinal node metastasis in squamous cell cancer of penis. | journal = World J Urol | volume = 28 | issue = 1 | pages = 93-8 | month = Feb | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s00345-009-0421-1 | PMID = 19488760 }}</ref> and changes the T-stage for pT1a tumours to pT1b. | ||
DDx: | |||
*[[Penile intraepithelial neoplasia]] (squamous dysplasia). | |||
*[[Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia]]. | |||
===Subtyping=== | |||
*''Non-HPV-related squamous cell carcinoma. | |||
**p16 -ve, p53 +ve.{{fact}} | |||
*''HPV-related squamous cell carcinoma''. | |||
**p16 +ve, p53 -ve.{{fact}} | |||
===Grading=== | |||
*G1 - well differentiated. § | |||
**Almost normal appearing - diagnosis of malignancy may be challenging. | |||
*G2 - moderately differentiated. § | |||
*G3 - poorly differentiated. | |||
**Anaplastic cells. | |||
**Typically little or no keratinization. | |||
*GX - cannot be assessed. | |||
Notes: | |||
*§ The differentiation between G1 and G2 is similar to [[squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck]]. | |||
*G2 (moderately differentiated) is the most common.<ref name=pmid24119832/> | |||
===Staging=== | |||
T-stage: | |||
*pT1a - subepithelial tissue involved, no [[LVI]], not poorly differentiated (G3). | |||
*pT1b - subepithelial tissue involved with [[LVI]] ''or'' poorly differentiated. | |||
*pT2 - corpus spongiosum or cavernosum involved. | |||
*pT3 - urethral involvement. | |||
*pT4 - adjacent structure(s) involved. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Squamous carcinoma of the penis -- low mag.jpg | Penile SCC - low mag. | |||
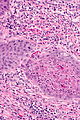
Image: Squamous carcinoma of the penis -- high mag.jpg | Penile SCC - high mag. | |||
Image: Squamous carcinoma of the penis - alt -- high mag.jpg | Penile SCC - high mag. | |||
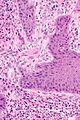
Image: Squamous carcinoma of the penis - 2 -- intermed mag.jpg | Penile SCC - intermed. mag. | |||
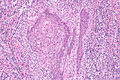
Image: Squamous carcinoma of the penis - 2 -- high mag.jpg | Penile SCC - high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | |||
*p16 +ve - in types associated with [[HPV]] (basaloid SCC, warty SCC and warty-basaloid SCC).<ref name=pmid22367299>{{Cite journal | last1 = Cubilla | first1 = AL. | last2 = Lloveras | first2 = B. | last3 = Alemany | first3 = L. | last4 = Alejo | first4 = M. | last5 = Vidal | first5 = A. | last6 = Kasamatsu | first6 = E. | last7 = Clavero | first7 = O. | last8 = Alvarado-Cabrero | first8 = I. | last9 = Lynch | first9 = C. | title = Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the penis with papillary features: a clinicopathologic study of 12 cases. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 36 | issue = 6 | pages = 869-75 | month = Jun | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318249c6f3 | PMID = 22367299 }}</ref> | |||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
===Biopsy=== | |||
<pre> | |||
Penis, Biopsy: | |||
- INVASIVE SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA, well differentiated. | |||
Comment: | |||
The tumour has differentiated penile intraepithelial neoplasia adjacent to it. The tumour is p16 negative and p53 positive. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Resection=== | |||
<pre> | |||
Tip of Penis, Partial Penectomy: | |||
- Invasive squamous cell carcinoma, moderately differentiated (G2). | |||
-- Invasion into the lamina propria. | |||
-- Surgical margins negative for dysplasia and negative for malignancy. | |||
-- TNM stage: pT1a pNx. | |||
-- Please see tumour summary. | |||
</pre> | |||
===All caps=== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
TIP OF PENIS, PARTIAL PENECTOMY: | TIP OF PENIS, PARTIAL PENECTOMY: | ||
| Line 71: | Line 136: | ||
COMMENT: | COMMENT: | ||
This lesion was previously excised. The surgical clearance is 1 mm. The tumour | This lesion was previously excised. The surgical clearance is 1 mm. The tumour | ||
thickness is approximately 4 mm. | thickness is approximately 4 mm. No lymphovascular invasion is identified. No | ||
lymphovascular invasion is identified. No corpus spongiosum or corpus cavernosum | |||
invasion is seen. The staging is unchanged. | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:19, 21 September 2021
| Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
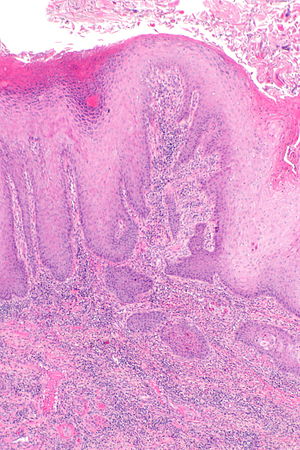 Squamous carcinoma of the penis. H&E stain. | |
| Subtypes | HPV-related SCC, Non-HPV-related SCC |
| LM DDx | penile intraepithelial neoplasia, pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia |
| Gross | mass lesion, scaly patches/nodules, usu. erythematous, +/-ulceration. |
| Grossing notes | penectomy |
| Site | penis |
|
| |
| Clinical history | uncircumcised |
| Prevalence | uncommon overall, most common form of penis cancer |
| Prognosis | good |
| Treatment | surgery |
Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis is the most common malignancy of the penis.
Penile cancer redirects to this article.
General
- Not very common overall.[1]
- Most common form of penile cancer.
- Non-squamous penis cancer only ~5% of cases.[2]
Epidemiology:[1]
- Median age ~ 67 years old.
- Usually a good outcome - 5 year cause specific survival ~ 81%.[1]
- Possible association with sex with animals.[3]
Gross
- Scaly patches/nodules.
- Usually erythematous.
- +/-Ulceration.
Microscopic
Features:
Notes:
- Lymphovascular invasion - prognostically important,[4] and changes the T-stage for pT1a tumours to pT1b.
DDx:
- Penile intraepithelial neoplasia (squamous dysplasia).
- Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia.
Subtyping
- Non-HPV-related squamous cell carcinoma.
- p16 -ve, p53 +ve.[citation needed]
- HPV-related squamous cell carcinoma.
- p16 +ve, p53 -ve.[citation needed]
Grading
- G1 - well differentiated. §
- Almost normal appearing - diagnosis of malignancy may be challenging.
- G2 - moderately differentiated. §
- G3 - poorly differentiated.
- Anaplastic cells.
- Typically little or no keratinization.
- GX - cannot be assessed.
Notes:
- § The differentiation between G1 and G2 is similar to squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
- G2 (moderately differentiated) is the most common.[1]
Staging
T-stage:
- pT1a - subepithelial tissue involved, no LVI, not poorly differentiated (G3).
- pT1b - subepithelial tissue involved with LVI or poorly differentiated.
- pT2 - corpus spongiosum or cavernosum involved.
- pT3 - urethral involvement.
- pT4 - adjacent structure(s) involved.
Images
IHC
Sign out
Biopsy
Penis, Biopsy: - INVASIVE SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA, well differentiated. Comment: The tumour has differentiated penile intraepithelial neoplasia adjacent to it. The tumour is p16 negative and p53 positive.
Resection
Tip of Penis, Partial Penectomy: - Invasive squamous cell carcinoma, moderately differentiated (G2). -- Invasion into the lamina propria. -- Surgical margins negative for dysplasia and negative for malignancy. -- TNM stage: pT1a pNx. -- Please see tumour summary.
All caps
TIP OF PENIS, PARTIAL PENECTOMY: - INVASIVE SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA, MODERATELY DIFFERENTIATED. -- SURGICAL MARGINS NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. -- PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY.
TIP OF PENIS, PARTIAL PENECTOMY: - INVASIVE SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA OF CORONAL SULCUS, MODERATELY DIFFERENTIATED. -- SURGICAL MARGINS NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. - LICHEN SCLEROSIS. - POST-SURGICAL CHANGES (GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION (NON-NECROTIZING), SIDEROPHAGES). COMMENT: This lesion was previously excised. The surgical clearance is 1 mm. The tumour thickness is approximately 4 mm. No lymphovascular invasion is identified. No lymphovascular invasion is identified. No corpus spongiosum or corpus cavernosum invasion is seen. The staging is unchanged.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Burt, LM.; Shrieve, DC.; Tward, JD. (Jan 2014). "Stage presentation, care patterns, and treatment outcomes for squamous cell carcinoma of the penis.". Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 88 (1): 94-100. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.08.013. PMID 24119832.
- ↑ Moses, KA.; Sfakianos, JP.; Winer, A.; Bernstein, M.; Russo, P.; Dalbagni, G. (Dec 2013). "Non-squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: single-center, 15-year experience.". World J Urol. doi:10.1007/s00345-013-1216-y. PMID 24292119.
- ↑ Zequi, Sde C.; Guimarães, GC.; da Fonseca, FP.; Ferreira, U.; de Matheus, WE.; Reis, LO.; Aita, GA.; Glina, S. et al. (Jul 2012). "Sex with animals (SWA): behavioral characteristics and possible association with penile cancer. A multicenter study.". J Sex Med 9 (7): 1860-7. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02512.x. PMID 22023719.
- ↑ Bhagat, SK.; Gopalakrishnan, G.; Kekre, NS.; Chacko, NK.; Kumar, S.; Manipadam, MT.; Samuel, P. (Feb 2010). "Factors predicting inguinal node metastasis in squamous cell cancer of penis.". World J Urol 28 (1): 93-8. doi:10.1007/s00345-009-0421-1. PMID 19488760.
- ↑ Cubilla, AL.; Lloveras, B.; Alemany, L.; Alejo, M.; Vidal, A.; Kasamatsu, E.; Clavero, O.; Alvarado-Cabrero, I. et al. (Jun 2012). "Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the penis with papillary features: a clinicopathologic study of 12 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 36 (6): 869-75. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318249c6f3. PMID 22367299.