Difference between revisions of "Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (another image) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| Micro = spindle cells with nuclear palisading, RBC extravasation | | Micro = spindle cells with nuclear palisading, RBC extravasation | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[schwannoma]] | | LMDDx = [[schwannoma]], [[leiomyoma]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = SMA +ve, S-100 -ve. | | IHC = SMA +ve, S-100 -ve. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
#Intracellular and extracellular fuchsinophilic bodies. | #Intracellular and extracellular fuchsinophilic bodies. | ||
#*Smooth muscle actin +ve. | #*Smooth muscle actin +ve. | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*''Fuchsinophilic'' = affinity for the acid dye fuchsin.<ref>URL: [http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/fuchsinophilic http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/fuchsinophilic]. Accessed on: 3 October 2011.</ref> | *''Fuchsinophilic'' = affinity for the acid dye fuchsin.<ref>URL: [http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/fuchsinophilic http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/fuchsinophilic]. Accessed on: 3 October 2011.</ref> | ||
**Image: [http://www.flickr.com/photos/53376324@N08/5387821397/in/photostream Fuchsinophilic material (flickr.com)] - red. | **Image: [http://www.flickr.com/photos/53376324@N08/5387821397/in/photostream Fuchsinophilic material (flickr.com)] - red. | ||
DDx:<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sarma | first1 = NH. | last2 = Arora | first2 = KS. | last3 = Varalaxmi | first3 = KP. | title = Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma: a case report and an update on etiopathogenesis and differential diagnosis. | journal = J Cancer Res Ther | volume = 9 | issue = 2 | pages = 295-8 | month = | year = | doi = 10.4103/0973-1482.113395 | PMID = 23771380 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Schwannoma]]. | |||
*[[Leiomyoma]]. | |||
*[[Leiomyosarcoma]]. | |||
*[[Malignant melanoma]]. | |||
*[[Kaposi sarcoma]]. | |||
*Metastatic carcinoma. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 68: | Line 73: | ||
Image: Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma - high mag.jpg | IPM - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image: Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma - high mag.jpg | IPM - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
Image: Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma - very high mag.jpg | IPM - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image: Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma - very high mag.jpg | IPM - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
Image: Intra-nodal palisaded myofibroblastoma.jpg | IPM - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
www: | www: | ||
| Line 77: | Line 83: | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
*SMA +ve. | *SMA +ve. | ||
*Cyclin D1 +ve. | *Vimentin +ve. | ||
*Cyclin D1 +ve/-ve.<ref name=pmid23771380>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sarma | first1 = NH. | last2 = Arora | first2 = KS. | last3 = Varalaxmi | first3 = KP. | title = Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma: a case report and an update on etiopathogenesis and differential diagnosis. | journal = J Cancer Res Ther | volume = 9 | issue = 2 | pages = 295-8 | month = | year = | doi = 10.4103/0973-1482.113395 | PMID = 23771380 }}</ref> | |||
Other: | Other: | ||
| Line 86: | Line 93: | ||
*Desmin -ve | *Desmin -ve | ||
*Ki-67 - low. | *Ki-67 - low. | ||
*HMB-45 -ve. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:54, 23 September 2018
| Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
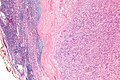
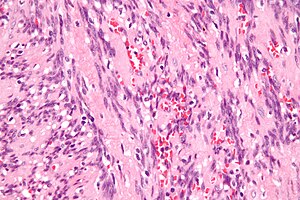 IPM. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | spindle cells with nuclear palisading, RBC extravasation |
| LM DDx | schwannoma, leiomyoma |
| IHC | SMA +ve, S-100 -ve. |
| Site | lymph node. |
|
| |
| Signs | mass lesion |
| Prevalence | very rare. |
| Clin. DDx | lymphoma, metastatic carcinoma. |
Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma, abbreviated IPM, is a rare tumour that classically presents as an inguinal mass.[1]
General
- Rare ~ 55 cases in the world literature.[2]
Demographics:
- Male:female = 2:1.
- Adults - middle age.
Location:
- Usually inguinal lymph node.
- Reported in retroperitoneum.[2]
Treatment:
- Simple excision; rare recurrences have been reported.[3]
Microscopic
Features:
- Rim of peripheral lymphoid tissue.
- Remnant of lymph node.
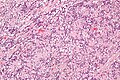
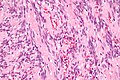
- Spindle cells with nuclear palisading - key feature.
- RBC extravasation/hemorrhage.
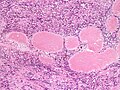
- Amianthoid fibers - blood vessel surrounded by collagen with (fine) peripheral spokes.[4]
- Paucicellular regions.[5]
- Intracellular and extracellular fuchsinophilic bodies.
- Smooth muscle actin +ve.
Notes:
- Fuchsinophilic = affinity for the acid dye fuchsin.[6]
- Image: Fuchsinophilic material (flickr.com) - red.
DDx:[7]
- Schwannoma.
- Leiomyoma.
- Leiomyosarcoma.
- Malignant melanoma.
- Kaposi sarcoma.
- Metastatic carcinoma.
Images
www:
- IPM (surgicalpathologyatlas.com).
- Amianthoid fibers (nih.gov).[4]
- Amianthoid fibers (nih.gov).[2]
- IPM - several images (upmc.edu).
IHC
- SMA +ve.
- Vimentin +ve.
- Cyclin D1 +ve/-ve.[8]
Other:
- S100 -ve
- Excludes schwannoma.
- GFAP -ve.
- CD34 -ve.
- Desmin -ve
- Ki-67 - low.
- HMB-45 -ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Nguyen, T.; Eltorky, MA. (Feb 2007). "Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 131 (2): 306-10. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2007)131[306:IPM]2.0.CO;2. PMID 17284119.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Sagar, J.; Vargiamidou, A.; Manikkapurath, H. (2011). "Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma originating from retroperitoneum: an unusual origin.". BMC Clin Pathol 11: 7. doi:10.1186/1472-6890-11-7. PMC 3146916. PMID 21718465. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3146916/.
- ↑ Creager, AJ.; Garwacki, CP. (May 1999). "Recurrent intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma with metaplastic bone formation.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 123 (5): 433-6. doi:10.1043/0003-9985(1999)1230433:RIPMWM2.0.CO;2. PMID 10235504.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bigotti, G.; Coli, A.; Mottolese, M.; Di Filippo, F. (Sep 1991). "Selective location of palisaded myofibroblastoma with amianthoid fibres.". J Clin Pathol 44 (9): 761-4. PMID 1918406.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case121/micro.html. Accessed on: 3 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/fuchsinophilic. Accessed on: 3 October 2011.
- ↑ Sarma, NH.; Arora, KS.; Varalaxmi, KP.. "Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma: a case report and an update on etiopathogenesis and differential diagnosis.". J Cancer Res Ther 9 (2): 295-8. doi:10.4103/0973-1482.113395. PMID 23771380.
- ↑ Sarma, NH.; Arora, KS.; Varalaxmi, KP.. "Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma: a case report and an update on etiopathogenesis and differential diagnosis.". J Cancer Res Ther 9 (2): 295-8. doi:10.4103/0973-1482.113395. PMID 23771380.