Difference between revisions of "Down syndrome"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+genetics) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Down syndrome''', is a common genetic abnormality. It may also be called '''Trisomy 21'''; however, technically this may not be completely correct in all cases. | '''Down syndrome''', abbreviated '''DS''', is a common genetic abnormality. It may also be called '''Trisomy 21'''; however, technically this may not be completely correct in all cases. | ||
==Genetics== | ==Genetics== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
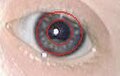
*Brushfield spots = white/grey spots in the iris (the "colour part" of the eye). | *Brushfield spots = white/grey spots in the iris (the "colour part" of the eye). | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Brushfield_eyes_magnified.jpg | Brushfield spots. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Simplified=== | |||
Simplified version of mnemonic ''CHILD HAS PROBLEM'': | |||
#[[congenital heart disease|'''C'''ongenital heart disease]]. | |||
#'''H'''ypothyroidism. | |||
#'''I'''ncurved 5th digit (clinodactyly) / Increased gap between 1st and 2nd toe. | |||
#[[Leukemia|'''L'''eukemia]] risk x2. | |||
#'''D'''uodenal atresia. | |||
#[[Hirschsprung disease|'''H'''irschsprung disease]]. | |||
#[[Alzheimer disease|'''A'''lzheimer disease]] / Alantoaxial instability. | |||
#'''S'''hort neck. | |||
#'''P'''almar crease / Protruding [[tongue]]. | |||
#'''R'''ound face. | |||
#'''O'''cciput flat / Oblique eye fissure. | |||
#'''B'''rushfield spots / Brachycephaly. | |||
#'''L'''ow nasal bridge. | |||
#'''E'''picanthic fold / Ears folded. | |||
#'''M'''ental retardation. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:25, 24 May 2013
Down syndrome, abbreviated DS, is a common genetic abnormality. It may also be called Trisomy 21; however, technically this may not be completely correct in all cases.
Genetics
Down syndrome can be the result of three different defects:[1]
| Defect | Percent of DS | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Extra chromosome 21 (trisomy 21) | ~95% | defect seen more often with increasing maternal age |
| Robertsonian translocation | ~4% | part of chromosome 21 attaches to chromosome 22 or 14; one parent is a carrier -- recurrence virtually 100%; no age dependence |
| Mosaicism | ~1% | some cells have a triple dose of chromosome 21 while others have a normal number of chromosome 21; no age dependence |
Characteristics
Mnemonic CHILD HAS PROBLEM:[2]
- Congenital heart disease / Cataracts.
- Hypothyroidism / Hypotonia.
- Incurved 5th digit (clinodactyly)[3] / Increased gap between 1st and 2nd toe.
- Leukemia risk x2 / Lung problem.
- Duodenal atresia / Delayed development.
- Hirschsprung disease / Hearing loss.
- Alzheimer disease / Alantoaxial instability.
- Short neck / Squint.
- Palmar crease / Protruding tongue.
- Round face / Rolling eye (nystagmus).
- Occiput flat / Oblique eye fissure.
- Brushfield spots / Brachycephaly.
- Low nasal bridge / Language problems.
- Epicanthic fold / Ears folded.
- Mental retardation / Myoclonus.
Notes:
- Brushfield spots = white/grey spots in the iris (the "colour part" of the eye).
Simplified
Simplified version of mnemonic CHILD HAS PROBLEM:
- Congenital heart disease.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Incurved 5th digit (clinodactyly) / Increased gap between 1st and 2nd toe.
- Leukemia risk x2.
- Duodenal atresia.
- Hirschsprung disease.
- Alzheimer disease / Alantoaxial instability.
- Short neck.
- Palmar crease / Protruding tongue.
- Round face.
- Occiput flat / Oblique eye fissure.
- Brushfield spots / Brachycephaly.
- Low nasal bridge.
- Epicanthic fold / Ears folded.
- Mental retardation.
See also
- Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome).
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome).
- Chromosomal anomalies.
- Stillbirth.
References
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 99. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ URL: http://www.valuemd.com/genetics.php. Accessed on: 29 May 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.handresearch.com/diagnostics/simian-line-down-syndrome.htm. Accessed on: 29 May 2011.