Difference between revisions of "Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+infobox) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
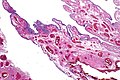
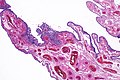
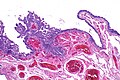
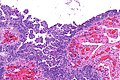
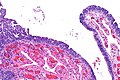
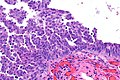
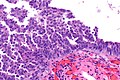
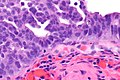
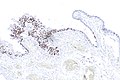
| Caption = Micrograph showing serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Micrograph showing serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = | ||
| Micro = | | Micro = three of the following five: (1) atypical chromatin pattern, (2) nuclear enlargement, (3) nuclear pleomorphism, (4) nuclear moulding, (5) loss of nuclear polarity ''or'' epithelial stratification | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = | | LMDDx = | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = | | IHC = p16 +ve, p53 +ve, Ki-67 increased | ||
| EM = | | EM = | ||
| Molecular = BRCA1 mutation or BRCA2 mutation | | Molecular = BRCA1 mutation or BRCA2 mutation | ||
| IF = | | IF = | ||
| Gross = | | Gross = not apparent on gross | ||
| Grossing = | | Grossing = | ||
| Staging = | | Staging = | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Syndromes = | | Syndromes = | ||
| Clinicalhx = | | Clinicalhx = | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = | ||
| Symptoms = none | | Symptoms = none | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
| Other = | | Other = | ||
| ClinDDx = | | ClinDDx = | ||
| Tx = | | Tx = | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma''', abbreviated '''STIC'''<ref name=pmid21989347>{{Cite journal | last1 = Visvanathan | first1 = K. | last2 = Vang | first2 = R. | last3 = Shaw | first3 = P. | last4 = Gross | first4 = A. | last5 = Soslow | first5 = R. | last6 = Parkash | first6 = V. | last7 = Shih | first7 = IeM. | last8 = Kurman | first8 = RJ. | title = Diagnosis of serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma based on morphologic and immunohistochemical features: a reproducibility study. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 35 | issue = 12 | pages = 1766-75 | month = Dec | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822f58bc | PMID = 21989347 }}</ref> (pronounced ''stick''), is considered to be the precursor of [[serous carcinoma]]. | '''Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma''', abbreviated '''STIC'''<ref name=pmid21989347>{{Cite journal | last1 = Visvanathan | first1 = K. | last2 = Vang | first2 = R. | last3 = Shaw | first3 = P. | last4 = Gross | first4 = A. | last5 = Soslow | first5 = R. | last6 = Parkash | first6 = V. | last7 = Shih | first7 = IeM. | last8 = Kurman | first8 = RJ. | title = Diagnosis of serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma based on morphologic and immunohistochemical features: a reproducibility study. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 35 | issue = 12 | pages = 1766-75 | month = Dec | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822f58bc | PMID = 21989347 }}</ref> (pronounced ''stick''), is considered to be the precursor of [[serous carcinoma]]. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*Atypical tubal lesion (STIL or TILT) - lack proliferation.{{fact}} | *Atypical tubal lesion (STIL or ''tubal intraepithelial lesions in transition'' (TILT)<ref>{{cite journal |authors=Nishida N, Murakami F, Higaki K |title=Detection of serous precursor lesions in resected fallopian tubes from patients with benign diseases and a relatively low risk for ovarian cancer |journal=Pathol Int |volume=66 |issue=6 |pages=337–42 |date=June 2016 |pmid=27250113 |doi=10.1111/pin.12419 |url=}}</ref>) - lack proliferation.{{fact}} | ||
*[[Serous carcinoma of the fallopian tube]]. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 70: | Line 71: | ||
Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma - alt -- high mag.jpg | STIC - high mag. (WC) | Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma - alt -- high mag.jpg | STIC - high mag. (WC) | ||
Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma -- very high mag.jpg | STIC - very high mag. (WC) | Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma -- very high mag.jpg | STIC - very high mag. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | |||
====www==== | |||
*[http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v23/n6/fig_tab/modpathol201060f1.html#figure-title STIC (nature.com)].<ref name=pmid20228782>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sehdev | first1 = AS. | last2 = Kurman | first2 = RJ. | last3 = Kuhn | first3 = E. | last4 = Shih | first4 = IeM. | title = Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma upregulates markers associated with high-grade serous carcinomas including Rsf-1 (HBXAP), cyclin E and fatty acid synthase. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 23 | issue = 6 | pages = 844-55 | month = Jun | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.2010.60 | PMID = 20228782 }}</ref> | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3148026/figure/F3/ STIC - schematic (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid21683865>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kurman | first1 = RJ. | last2 = Shih | first2 = IeM. | title = Molecular pathogenesis and extraovarian origin of epithelial ovarian cancer--shifting the paradigm. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 42 | issue = 7 | pages = 918-31 | month = Jul | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1016/j.humpath.2011.03.003 | PMID = 21683865 }}</ref> | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3148026/figure/F6/ STIC and STIL with p53 stain (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid21683865/> | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3148026/figure/F5/ STIC - p53 stain (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid21683865/> | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2860809/figure/fig1/ Small STIC - H&E and p53 (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid20445756>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gross | first1 = AL. | last2 = Kurman | first2 = RJ. | last3 = Vang | first3 = R. | last4 = Shih | first4 = IeM. | last5 = Visvanathan | first5 = K. | title = Precursor lesions of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma: morphological and molecular characteristics. | journal = J Oncol | volume = 2010 | issue = | pages = 126295 | month = | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1155/2010/126295 | PMID = 20445756 }}</ref> | |||
*[http://www.ovariancancerprevention.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/10/apotosis-and-mitosis-in-STIC.jpg STIC - high mag. (ovariancancerprevention.org)].<ref>URL: [http://www.ovariancancerprevention.org/?page_id=191 http://www.ovariancancerprevention.org/?page_id=191]. Accessed on: 13 May 2014.</ref> | |||
*[http://www.ovariancancerprevention.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/10/STIC-junction-HM.jpg STIC & benign - high mag. (ovariancancerprevention.org)]. | |||
==IHC== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid21989347/> | |||
*p53 +ve. | |||
*Ki-67 increased ~10%. (???) | |||
*p16 +ve.<ref name=pmid20228782/> | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
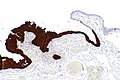
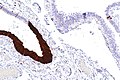
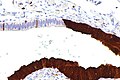
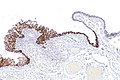
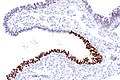
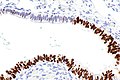
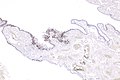
Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma - p16 -- very low mag.jpg | STIC - p16 - very low mag. (WC) | Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma - p16 -- very low mag.jpg | STIC - p16 - very low mag. (WC) | ||
Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma - p16 -- low mag.jpg | STIC - p16 - low mag. (WC) | Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma - p16 -- low mag.jpg | STIC - p16 - low mag. (WC) | ||
| Line 85: | Line 103: | ||
Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma - Ki-67 -- high mag.jpg | STIC - Ki-67 - high mag. (WC) | Image: Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma - Ki-67 -- high mag.jpg | STIC - Ki-67 - high mag. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 05:17, 4 November 2024
| Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
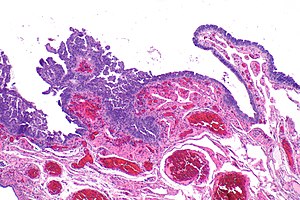 Micrograph showing serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | three of the following five: (1) atypical chromatin pattern, (2) nuclear enlargement, (3) nuclear pleomorphism, (4) nuclear moulding, (5) loss of nuclear polarity or epithelial stratification |
| IHC | p16 +ve, p53 +ve, Ki-67 increased |
| Molecular | BRCA1 mutation or BRCA2 mutation |
| Gross | not apparent on gross |
| Site | fallopian tubes |
|
| |
| Symptoms | none |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma, abbreviated STIC[1] (pronounced stick), is considered to be the precursor of serous carcinoma.
It is also known as tubal intraepithelial carcinoma.
General
- Considered the precursor lesion for tubal serous carcinoma.[2]
- Seen in ~6% of prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomies in BRCA-mutation carriers.[3]
Gross
- Not apparent on gross.
- Usually at the fimbriated end of the tube.
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Discrete papillary growth - low power.
- Formal criteria - need 3 or more:
- Atypical chromatin pattern.
- Nuclear enlargement.
- Nuclear pleomorphism.
- Nuclear moulding.
- Loss of nuclear polarity or epithelial stratification.
Notes:
- At low power STIC is usually tall cells that are too blue.
- Cilia suggest benign.
DDx:
- Atypical tubal lesion (STIL or tubal intraepithelial lesions in transition (TILT)[5]) - lack proliferation.[citation needed]
- Serous carcinoma of the fallopian tube.
Images
www
- STIC (nature.com).[4]
- STIC - schematic (nih.gov).[6]
- STIC and STIL with p53 stain (nih.gov).[6]
- STIC - p53 stain (nih.gov).[6]
- Small STIC - H&E and p53 (nih.gov).[7]
- STIC - high mag. (ovariancancerprevention.org).[8]
- STIC & benign - high mag. (ovariancancerprevention.org).
IHC
Features:[1]
- p53 +ve.
- Ki-67 increased ~10%. (???)
- p16 +ve.[4]
Images
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Visvanathan, K.; Vang, R.; Shaw, P.; Gross, A.; Soslow, R.; Parkash, V.; Shih, IeM.; Kurman, RJ. (Dec 2011). "Diagnosis of serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma based on morphologic and immunohistochemical features: a reproducibility study.". Am J Surg Pathol 35 (12): 1766-75. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822f58bc. PMID 21989347.
- ↑ Lee, Y.; Miron, A.; Drapkin, R.; Nucci, MR.; Medeiros, F.; Saleemuddin, A.; Garber, J.; Birch, C. et al. (Jan 2007). "A candidate precursor to serous carcinoma that originates in the distal fallopian tube.". J Pathol 211 (1): 26-35. doi:10.1002/path.2091. PMID 17117391.
- ↑ Mingels MJ, Roelofsen T, van der Laak JA, et al. (October 2012). "Tubal epithelial lesions in salpingo-oophorectomy specimens of BRCA-mutation carriers and controls". Gynecol. Oncol. 127 (1): 88–93. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.06.015. PMID 22710074.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Sehdev, AS.; Kurman, RJ.; Kuhn, E.; Shih, IeM. (Jun 2010). "Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma upregulates markers associated with high-grade serous carcinomas including Rsf-1 (HBXAP), cyclin E and fatty acid synthase.". Mod Pathol 23 (6): 844-55. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.60. PMID 20228782.
- ↑ Nishida N, Murakami F, Higaki K (June 2016). "Detection of serous precursor lesions in resected fallopian tubes from patients with benign diseases and a relatively low risk for ovarian cancer". Pathol Int 66 (6): 337–42. doi:10.1111/pin.12419. PMID 27250113.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Kurman, RJ.; Shih, IeM. (Jul 2011). "Molecular pathogenesis and extraovarian origin of epithelial ovarian cancer--shifting the paradigm.". Hum Pathol 42 (7): 918-31. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2011.03.003. PMID 21683865.
- ↑ Gross, AL.; Kurman, RJ.; Vang, R.; Shih, IeM.; Visvanathan, K. (2010). "Precursor lesions of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma: morphological and molecular characteristics.". J Oncol 2010: 126295. doi:10.1155/2010/126295. PMID 20445756.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ovariancancerprevention.org/?page_id=191. Accessed on: 13 May 2014.