Difference between revisions of "Foveolar type dysplasia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+SO +IHC) |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Tall columnar cells with basal nuclei in a villiform architecture.<ref name=pmid20228780/> | *Tall columnar cells with basal nuclei in a villiform architecture.<ref name=pmid20228780/> | ||
*+/-Proliferative activity - mitotic figures. | |||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
| Line 53: | Line 54: | ||
www: | www: | ||
*[http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v23/n6/fig_tab/modpathol201059f2.html Foveolar type dysplasia of the esophagus (nature.com)].<ref name=pmid20228780>{{Cite journal | last1 = Brown | first1 = IS. | last2 = Whiteman | first2 = DC. | last3 = Lauwers | first3 = GY. | title = Foveolar type dysplasia in Barrett esophagus. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 23 | issue = 6 | pages = 834-43 | month = Jun | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.2010.59 | PMID = 20228780 }}</ref> | *[http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v23/n6/fig_tab/modpathol201059f2.html Foveolar type dysplasia of the esophagus (nature.com)].<ref name=pmid20228780>{{Cite journal | last1 = Brown | first1 = IS. | last2 = Whiteman | first2 = DC. | last3 = Lauwers | first3 = GY. | title = Foveolar type dysplasia in Barrett esophagus. | journal = Mod Pathol | volume = 23 | issue = 6 | pages = 834-43 | month = Jun | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1038/modpathol.2010.59 | PMID = 20228780 }}</ref> | ||
==IHC== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid17419219>{{cite journal |authors=Testino G, Cornaggia M, Ferrando V |title=Low- and high-grade non-invasive gastric neoplasia (formerly dysplasia): cytological differentiation (gastro-entero-pancreatic antigens) in association with p53 pattern expression |journal=Hepatogastroenterology |volume=54 |issue=73 |pages=1–3 |date=2007 |pmid=17419219 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
*p53 +ve. | |||
*Ki-67 increased staining in ~100% of cases. | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
A. Polyp, Stomach, Biopsy or Polypectomy: | |||
- Polypoid fragment of gastric body type mucosa with low-grade DYSPLASIA, foveolar type, see comment. | |||
- NEGATIVE for Helicobacter-like organisms. | |||
- NEGATIVE for intestinal metaplasia. | |||
- NEGATIVE for evidence of malignancy. | |||
Comment: | |||
The sections show foveolar type epithelium with proliferation and hyperchromasia extending to the surface. A p53 and Ki-67 show diffuse staining in the abnormal epithelium. The architectural complexity is mild in the abnormal epithelium. Deepers were cut (x3); these are non-contributory. | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 22:16, 18 December 2023
| Foveolar type dysplasia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
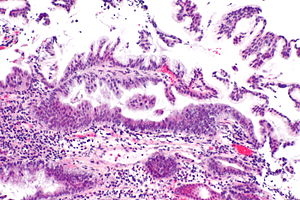 Foveolar dysplasia of the duodenum. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | type 2 dysplasia, foveolar dysplasia, foveolar/hyperplastic dysplasia |
| LM DDx | benign foveolar epithelium, gastric heterotopia (if not stomach), benign ampullary epithelium, hyperplastic polyp |
| Site | stomach, duodenum (esp. ampulla of Vater), esophagus |
|
| |
| Syndromes | familial adenomatous polyposis |
|
| |
| Prevalence | not common |
| Other | may be subtle |
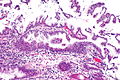
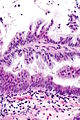
Foveolar type dysplasia, also foveolar dysplasia, is a form of dysplasia that arises from the foveolar cells, typically seen in the stomach. It may be subtle to unaccustomed eyes.
It is also described as non-adenomatous dysplasia, type 2 dysplasia and foveolar/hyperplastic type dysplasia.[1]
General
- Precursor to adenocarcinoma.
Microscopic
Features:
- Tall columnar cells with basal nuclei in a villiform architecture.[1]
- +/-Proliferative activity - mitotic figures.
DDx:
- Benign foveolar epithelium - seen in stomach and ampulla of Vater.
- Gastric heterotopia.
- Hyperplastic polyp.
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[2]
- p53 +ve.
- Ki-67 increased staining in ~100% of cases.
Sign out
A. Polyp, Stomach, Biopsy or Polypectomy: - Polypoid fragment of gastric body type mucosa with low-grade DYSPLASIA, foveolar type, see comment. - NEGATIVE for Helicobacter-like organisms. - NEGATIVE for intestinal metaplasia. - NEGATIVE for evidence of malignancy. Comment: The sections show foveolar type epithelium with proliferation and hyperchromasia extending to the surface. A p53 and Ki-67 show diffuse staining in the abnormal epithelium. The architectural complexity is mild in the abnormal epithelium. Deepers were cut (x3); these are non-contributory.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Brown, IS.; Whiteman, DC.; Lauwers, GY. (Jun 2010). "Foveolar type dysplasia in Barrett esophagus.". Mod Pathol 23 (6): 834-43. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.59. PMID 20228780.
- ↑ Testino G, Cornaggia M, Ferrando V (2007). "Low- and high-grade non-invasive gastric neoplasia (formerly dysplasia): cytological differentiation (gastro-entero-pancreatic antigens) in association with p53 pattern expression". Hepatogastroenterology 54 (73): 1–3. PMID 17419219.