Difference between revisions of "Vocal cord nodule"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Laryngeal nodule | | Caption = Laryngeal nodule | ||
| Synonyms = singer's nodule | | Synonyms = singer's nodule, vocal fold nodule | ||
| Micro = | | Micro = early: edema, fibroblasts proliferation; late: subepithelial hyaline / stromal hyaline, blood vessels - dilated | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[amyloidosis]], [[granular cell tumour]], spindle cell [[squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck|squamous cell carcinoma]], myxoma, ductal-type cyst | | LMDDx = [[amyloidosis]], [[granular cell tumour]], spindle cell [[squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck|squamous cell carcinoma]], myxoma, ductal-type cyst | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = [[congo red stain|congo red]] -ve | ||
| IHC = | | IHC = | ||
| EM = | | EM = | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| Gross = | | Gross = | ||
| Grossing = | | Grossing = | ||
| Site = vocal cord - see ''[[head and neck pathology]]'' | | Site = [[vocal cord]] - also see ''[[head and neck pathology]]'' | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Syndromes = | | Syndromes = | ||
| Clinicalhx = | | Clinicalhx = | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = +/-hoarseness | ||
| Symptoms = | | Symptoms = | ||
| Prevalence = common | | Prevalence = common | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| Tx = | | Tx = | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Vocal cord nodule''', also '''vocal cord polyp''' and '''singer's nodule''', is a benign pathology of the [[head and neck pathology|head and neck]]. | '''Vocal cord nodule''', also '''vocal cord polyp''', '''vocal fold nodule''' and '''singer's nodule''', is a benign pathology of the [[head and neck pathology|head and neck]]. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Benign. | *Benign. | ||
*Etiology: overuse, "phonatory trauma"<ref name=pmid19730264>{{Cite journal | last1 = Karkos | first1 = PD. | last2 = McCormick | first2 = M. | title = The etiology of vocal fold nodules in adults. | journal = Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg | volume = 17 | issue = 6 | pages = 420-3 | month = Dec | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1097/MOO.0b013e328331a7f8 | PMID = 19730264 }}</ref> (yelling). | |||
*Etiology: overuse, | |||
Clinical: | Clinical: | ||
| Line 67: | Line 66: | ||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
<pre> | |||
Left Vocal Cord Polyp, Excision: | |||
- Stratified squamous epithelium with compact hyperkeratosis and stromal | |||
edema, consistent with benign vocal cord nodule or polyp. | |||
- NEGATIVE for malignancy. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Block letters=== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
VOCAL CORD LESION, EXCISION: | VOCAL CORD LESION, EXCISION: | ||
Latest revision as of 18:27, 11 December 2023
| Vocal cord nodule | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Laryngeal nodule | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | singer's nodule, vocal fold nodule |
|
| |
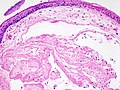
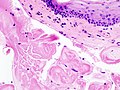
| LM | early: edema, fibroblasts proliferation; late: subepithelial hyaline / stromal hyaline, blood vessels - dilated |
| LM DDx | amyloidosis, granular cell tumour, spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma, myxoma, ductal-type cyst |
| Stains | congo red -ve |
| Site | vocal cord - also see head and neck pathology |
|
| |
| Signs | +/-hoarseness |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
Vocal cord nodule, also vocal cord polyp, vocal fold nodule and singer's nodule, is a benign pathology of the head and neck.
General
- Benign.
- Etiology: overuse, "phonatory trauma"[1] (yelling).
Clinical:
- Hoarseness.[2]
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Early:
- Edema.
- Fibroblasts proliferation.
- Late:
- Subepithelial hyaline / stromal hyaline.
- Blood vessels - dilated.
Notes:
- No inflammation.
DDx:[4]
- Amyloidosis.
- Granular cell tumour.
- Spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma.[5]
- Myxoma.
- Ductal-type cyst.
- Rheumatoid nodule.[6]
Images
Sign out
Left Vocal Cord Polyp, Excision: - Stratified squamous epithelium with compact hyperkeratosis and stromal edema, consistent with benign vocal cord nodule or polyp. - NEGATIVE for malignancy.
Block letters
VOCAL CORD LESION, EXCISION: - STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM WITH PARAKERATOSIS AND STROMAL EDEMA, CONSISTENT WITH BENIGN VOCAL CORD NODULE OR POLYP. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
VOCAL CORD LESION, EXCISION: - STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM WITH PARAKERATOSIS AND SUBEPITHELIAL HYALINE MATERIAL, CONSISTENT WITH WITH VOCAL CORD NODULE OR POLYP. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
See also
References
- ↑ Karkos, PD.; McCormick, M. (Dec 2009). "The etiology of vocal fold nodules in adults.". Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 17 (6): 420-3. doi:10.1097/MOO.0b013e328331a7f8. PMID 19730264.
- ↑ Müller, R. (Nov 1995). "[Hoarseness].". Ther Umsch 52 (11): 759-62. PMID 7502253.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970310-2. Accessed on: 4 February 2011.
- ↑ Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Head and Neck Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 9. ISBN 978-0443069604.
- ↑ Soylu, L.; Aydogan, B.; Tunali, N.; Ozsahinoglu, C. (Aug 1999). "Report of a rare case of vocal fold carcinoma that was obscured by a prominent vocal fold polyp.". Ear Nose Throat J 78 (8): 601-2. PMID 10485155.
- ↑ Abdou, AG.; Asaad, NY. (Oct 2012). "Rheumatoid nodule of the vocal cord.". Int J Surg Pathol 20 (5): 481-2. doi:10.1177/1066896912448426. PMID 22674917.