Difference between revisions of "Merkel cell carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(tweak) |
m (many ALK1 +ve) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
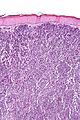
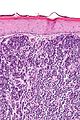
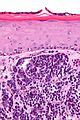
| Caption = Merkel cell carcinoma. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Merkel cell carcinoma. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Micro = neuroendocrine nuclear features (round nucleus, small nucleoli/no nucleolus, stippled chromatin), usually small (~3x resting lymphocyte), often in sheets | | Micro = neuroendocrine nuclear features (round nucleus, small nucleoli/no nucleolus, stippled chromatin), usually scant cytoplasm, usually small (~3x resting lymphocyte), often in sheets | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[small cell carcinoma]] | | LMDDx = [[small cell carcinoma]], cutaneous [[Ewing sarcoma]], [[Burkitt lymphoma]], other [[small round blue cell tumours]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = Merkel cell polyomavirus +ve, CK20 +ve (perinuclear dot-like), CD56 +ve, TTF-1 -ve, CK7 -ve | | IHC = Merkel cell polyomavirus +ve, CK20 +ve (perinuclear dot-like), CD56 +ve, TTF-1 -ve, CK7 -ve, NF +ve | ||
| EM = | | EM = | ||
| Molecular = | | Molecular = | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Syndromes = | | Syndromes = | ||
| Clinicalhx = | | Clinicalhx = +/-immunosuppressed/immunoincompetent | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = | ||
| Symptoms = | | Symptoms = | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
| Other = | | Other = | ||
| ClinDDx = | | ClinDDx = | ||
}} | |||
{{ Infobox external links | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| EHVSC = | |||
| EHVSC_mult = | |||
| pathprotocols = | |||
| wikipedia = merkel cell carcinoma | |||
| pathoutlines = | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Merkel cell carcinoma''', abbreviated '''MCC''', is an uncommon aggressive form of skin cancer. | '''Merkel cell carcinoma''', abbreviated '''MCC''', is an uncommon aggressive form of skin cancer. | ||
| Line 88: | Line 96: | ||
*AE1/AE3 +ve. | *AE1/AE3 +ve. | ||
*Merkel cell polyomavirus +ve ~85% of cases.<ref name=pmid21870327>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jung | first1 = HS. | last2 = Choi | first2 = YL. | last3 = Choi | first3 = JS. | last4 = Roh | first4 = JH. | last5 = Pyon | first5 = JK. | last6 = Woo | first6 = KJ. | last7 = Lee | first7 = EH. | last8 = Jang | first8 = KT. | last9 = Han | first9 = J. | title = Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinomas and small cell carcinomas by PCR and immunohistochemistry. | journal = Histol Histopathol | volume = 26 | issue = 10 | pages = 1231-41 | month = Oct | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21870327 }}</ref> | *Merkel cell polyomavirus +ve ~85% of cases.<ref name=pmid21870327>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jung | first1 = HS. | last2 = Choi | first2 = YL. | last3 = Choi | first3 = JS. | last4 = Roh | first4 = JH. | last5 = Pyon | first5 = JK. | last6 = Woo | first6 = KJ. | last7 = Lee | first7 = EH. | last8 = Jang | first8 = KT. | last9 = Han | first9 = J. | title = Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinomas and small cell carcinomas by PCR and immunohistochemistry. | journal = Histol Histopathol | volume = 26 | issue = 10 | pages = 1231-41 | month = Oct | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 21870327 }}</ref> | ||
*NF +ve (12 of 13 cases).<ref name=pmid16625069>{{cite journal |authors=Bobos M, Hytiroglou P, Kostopoulos I, Karkavelas G, Papadimitriou CS |title=Immunohistochemical distinction between merkel cell carcinoma and small cell carcinoma of the lung |journal=Am J Dermatopathol |volume=28 |issue=2 |pages=99–104 |date=April 2006 |pmid=16625069 |doi=10.1097/01.dad.0000183701.67366.c7 |url=}}</ref> | |||
**Useful to differentiate from [[small cell carcinoma of lung]]. | |||
Others: | Others: | ||
*TTF-1 -ve. | *TTF-1 -ve. | ||
*NSE +ve.<ref name=pmid15606676/> | *NSE +ve.<ref name=pmid15606676/> | ||
*PAX5 +ve.<ref name=pmid25040178>{{Cite journal | last1 = Jankowski | first1 = M. | last2 = Kopinski | first2 = P. | last3 = Schwartz | first3 = R. | last4 = Czajkowski | first4 = R. | title = Merkel cell carcinoma: is this a true carcinoma? | journal = Exp Dermatol | volume = 23 | issue = 11 | pages = 792-4 | month = Nov | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1111/exd.12490 | PMID = 25040178 }}</ref> | |||
*ALK1<ref name=pmid23574788>{{cite journal |vauthors=Filtenborg-Barnkob BE, Bzorek M |title=Expression of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in Merkel cell carcinomas |journal=Hum Pathol |volume=44 |issue=8 |pages=1656–64 |date=August 2013 |pmid=23574788 |doi=10.1016/j.humpath.2012.11.021 |url=}}</ref> | |||
==EM== | ==EM== | ||
| Line 99: | Line 111: | ||
*[[Dermatologic neoplasms]]. | *[[Dermatologic neoplasms]]. | ||
*[[Small cell carcinoma]]. | *[[Small cell carcinoma]]. | ||
*[[Dermatopathology]]. | |||
*[[Viruses and cancer]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:32, 10 January 2023
| Merkel cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Merkel cell carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | neuroendocrine nuclear features (round nucleus, small nucleoli/no nucleolus, stippled chromatin), usually scant cytoplasm, usually small (~3x resting lymphocyte), often in sheets |
| LM DDx | small cell carcinoma, cutaneous Ewing sarcoma, Burkitt lymphoma, other small round blue cell tumours |
| IHC | Merkel cell polyomavirus +ve, CK20 +ve (perinuclear dot-like), CD56 +ve, TTF-1 -ve, CK7 -ve, NF +ve |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Clinical history | +/-immunosuppressed/immunoincompetent |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | poor |
| Merkel cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| Wikipedia | merkel cell carcinoma |
Merkel cell carcinoma, abbreviated MCC, is an uncommon aggressive form of skin cancer.
General
Features:[1]
- Rare.
- Aggressive course/poor prognosis.
- Neuroendocrine-like.[2]
Etiology:
- Most caused by Merkel cell polyomavirus.[3][1]
- Immunocompromised/immunosuppressed (e.g. organ transplant recipients).
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Neuroendocrine nuclear features - round nucleus, small nucleoli/no nucleolus, stippled chromatin - key feature.
- Typically medium size cells ~3x resting lymphocyte.
- May be small or large.
- Architecture: nests, sheets or trabeculae.
- Scant cytoplasm.
- Abundant mitoses. †
- +/-Nuclear moulding.
- Nuclei of adjacent cells conform to one another.
- +/-Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes. ‡
Notes:
- † >10 mitoses/HPF = poor prognosis - definition suffers from HPFitis.[5]
- ‡ May be associated with a worse prognosis.[5]
- Merkel cell carcinoma lymph node metastases is difficult to diagnose with routine stains; use of IHC stains are advised.[5]
- Arise from the epidermis - very rarely in situ.[6]
DDx:
- Basal cell carcinoma - no stippled chromatin, less mitoses active.
- Cutaneous Ewing sarcoma - sorted-out with immunostains.
- Lymphoma.
- Metastatic small cell carcinoma.
- Other small round cell tumours.
Images
www:
- MCC (bccancer.bc.ca).
- MCC (joplink.net).
- Merkel cell carcinoma (ispub.com).
- Merkel cell carcinoma - several images (upmc.edu).
IHC
Features:
- CK7 -ve.
- CK20 +ve (perinuclear dot-like).[7]
- CAM5.2 +ve (dot-like pattern).
- CD56 +ve.
- AE1/AE3 +ve.
- Merkel cell polyomavirus +ve ~85% of cases.[8]
- NF +ve (12 of 13 cases).[9]
- Useful to differentiate from small cell carcinoma of lung.
Others:
EM
- Neurosecretory granules (AKA dense-core granules).[12]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Calder, KB.; Smoller, BR. (May 2010). "New insights into merkel cell carcinoma.". Adv Anat Pathol 17 (3): 155-61. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181d97836. PMID 20418670.
- ↑ Pulitzer, MP.; Amin, BD.; Busam, KJ. (May 2009). "Merkel cell carcinoma: review.". Adv Anat Pathol 16 (3): 135-44. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3181a12f5a. PMID 19395876.
- ↑ Feng, H.; Shuda, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, PS. (Feb 2008). "Clonal integration of a polyomavirus in human Merkel cell carcinoma.". Science 319 (5866): 1096-100. doi:10.1126/science.1152586. PMID 18202256.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 491. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 URL: /2011/SkinMerkelCell_11protocol.pdf http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/SkinMerkelCell_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 28 March 2012.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Ferringer, T.; Rogers, HC.; Metcalf, JS. (Feb 2005). "Merkel cell carcinoma in situ.". J Cutan Pathol 32 (2): 162-5. doi:10.1111/j.0303-6987.2005.00270.x. PMID 15606676.
- ↑ Leech, SN.; Kolar, AJ.; Barrett, PD.; Sinclair, SA.; Leonard, N. (Sep 2001). "Merkel cell carcinoma can be distinguished from metastatic small cell carcinoma using antibodies to cytokeratin 20 and thyroid transcription factor 1.". J Clin Pathol 54 (9): 727-9. PMID 11533085.
- ↑ Jung, HS.; Choi, YL.; Choi, JS.; Roh, JH.; Pyon, JK.; Woo, KJ.; Lee, EH.; Jang, KT. et al. (Oct 2011). "Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinomas and small cell carcinomas by PCR and immunohistochemistry.". Histol Histopathol 26 (10): 1231-41. PMID 21870327.
- ↑ Bobos M, Hytiroglou P, Kostopoulos I, Karkavelas G, Papadimitriou CS (April 2006). "Immunohistochemical distinction between merkel cell carcinoma and small cell carcinoma of the lung". Am J Dermatopathol 28 (2): 99–104. doi:10.1097/01.dad.0000183701.67366.c7. PMID 16625069.
- ↑ Jankowski, M.; Kopinski, P.; Schwartz, R.; Czajkowski, R. (Nov 2014). "Merkel cell carcinoma: is this a true carcinoma?". Exp Dermatol 23 (11): 792-4. doi:10.1111/exd.12490. PMID 25040178.
- ↑ "Expression of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in Merkel cell carcinomas". Hum Pathol 44 (8): 1656–64. August 2013. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2012.11.021. PMID 23574788.
- ↑ Gil-Moreno, A.; Garcia-Jiménez, A.; González-Bosquet, J.; Esteller, M.; Castellví-Vives, J.; Martínez Palones, JM.; Xercavins, J. (Mar 1997). "Merkel cell carcinoma of the vulva.". Gynecol Oncol 64 (3): 526-32. PMID 9062165.