Difference between revisions of "Placental alkaline phosphatase"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+infobox) |
|||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
*[[Seminoma]]. | *[[Seminoma]]. | ||
*[[Embryonal carcinoma]]. | *[[Embryonal carcinoma]]. | ||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
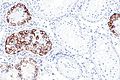
Image: ITGCN and Sertoli cells only - PLAP -- intermed mag.jpg | [[Germ cell neoplasia in situ]] (GCNIS) & [[Sertoli cells only]] (SCO) - intermed. mag. | |||
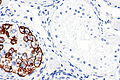
Image: ITGCN and Sertoli cells only - PLAP -- high mag.jpg | GCNIS & SCO - high mag. | |||
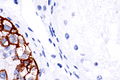
Image: ITGCN and Sertoli cells only - PLAP -- very high mag.jpg | GCNIS & SCO - very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 8 January 2017
| Placental alkaline phosphatase | |
|---|---|
| Immunostain in short | |
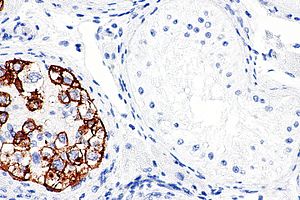 PLAP in germ cell neoplasia in situ - left of image. (WC) | |
| Abbreviation | PLAP |
| Similar stains | OCT4, OCT3/4 |
| Use | germ cell tumours |
| Subspeciality | genitourinary pathology, gynecologic pathology |
| Normal staining pattern | membranous |
| Positive | germ cell neoplasia in situ (previously ITGCN), seminoma, embryonal carcinoma |
Placental alkaline phosphatase, abbreviated PLAP, is a common immunostain used for assessing suspected germ cell tumours.
It has largely been replaced by OCT4.
Negative
Positive
- Germ cell neoplasia in situ (intratubular germ cell neoplasia).[2]
- Seminoma.
- Embryonal carcinoma.
Images
Germ cell neoplasia in situ (GCNIS) & Sertoli cells only (SCO) - intermed. mag.
See also
References
- ↑ Hawkins, E.; Heifetz, SA.; Giller, R.; Cushing, B. (Apr 1997). "The prepubertal testis (prenatal and postnatal): its relationship to intratubular germ cell neoplasia: a combined Pediatric Oncology Group and Children's Cancer Study Group.". Hum Pathol 28 (4): 404-10. PMID 9104938.
- ↑ Schreiber, L.; Lifschitz-Mercer, B.; Paz, G.; Yavetz, H.; Elliott, DJ.; Kula, K.; Slowikowska-Hilczer, J.; Maymon, BB. (Jan 2003). "Double immunolabeling by the RBM and the PLAP markers for identifying intratubular (in situ) germ cell neoplasia of the testis.". Int J Surg Pathol 11 (1): 17-20. PMID 12598912.