Difference between revisions of "Pregnancy luteoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split out) |
(→Gross) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
*Yellow. | *Yellow. | ||
Images: | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | |||
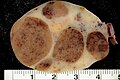
Image:Luteoma-of-pregnancy.jpg | Luteoma of pregnancy. (WC/Ed Uthman) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/78147607@N00/4730745138 Pregnancy luteoma (flickr.com/euthman)]. | *[http://www.flickr.com/photos/78147607@N00/4730745138 Pregnancy luteoma (flickr.com/euthman)]. | ||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/euthman/4730754894/in/photostream/ Pregnancy luteoma (flickr.com/euthman)]. | *[http://www.flickr.com/photos/euthman/4730754894/in/photostream/ Pregnancy luteoma (flickr.com/euthman)]. | ||
Latest revision as of 23:16, 7 January 2016
Pregnancy luteoma, also luteoma of pregnancy, is a rare benign ovarian tumour that arises in pregnancy.
General
- Tumour of pregnancy.
- Benign.
- Regress after pregnancy; thus, conservative management.[1]
Clinical:
Gross
- Solid.
- Yellow.
Images
www:
Microscopic
Features:
- Sheets of cells.
- Cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm, round nuclei and prominent nucleoli.
DDx:
Images
IHC
- Inhibin +ve.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Masarie, K.; Katz, V.; Balderston, K. (Sep 2010). "Pregnancy luteomas: clinical presentations and management strategies.". Obstet Gynecol Surv 65 (9): 575-82. doi:10.1097/OGX.0b013e3181f8c41d. PMID 21144088.
- ↑ Kao, HW.; Wu, CJ.; Chung, KT.; Wang, SR.; Chen, CY.. "MR imaging of pregnancy luteoma: a case report and correlation with the clinical features.". Korean J Radiol 6 (1): 44-6. PMID 15782020.
- ↑ Rodriguez, M.; Harrison, TA.; Nowacki, MR.; Saltzman, AK. (Nov 1999). "Luteoma of pregnancy presenting with massive ascites and markedly elevated CA 125.". Obstet Gynecol 94 (5 Pt 2): 854. PMID 10546765.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Qin, JL.; Qian, ZD.; Huang, LL. (2015). "Pregnancy luteoma followed with massive ascites and elevated CA125 after ovulation induction therapy: a case report and review of literatures.". Int J Clin Exp Med 8 (1): 1491-3. PMID 25785161.