Difference between revisions of "Secretory carcinoma of the salivary gland"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→IHC: update) |
(+image) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
| Image = | | Image = Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma (H&E, medium power).jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = | | Caption = Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma. [[H&E stain]]. (WC/NormanDy) | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = | ||
| Micro = large cells with abundant cytoplasm, small nuclei, +/-lymphocytic infiltrate, solid and microcystic growth pattern | | Micro = large cells with abundant cytoplasm, small nuclei, +/-lymphocytic infiltrate, solid and microcystic growth pattern | ||
Revision as of 02:22, 4 November 2015
| Secretory carcinoma of the salivary gland | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
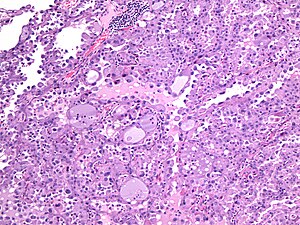 Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma. H&E stain. (WC/NormanDy) | |
|
| |
| LM | large cells with abundant cytoplasm, small nuclei, +/-lymphocytic infiltrate, solid and microcystic growth pattern |
| LM DDx | acinic cell carcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
| Stains | PAS +ve |
| IHC | S-100 +ve, mammomglobin +ve, vimentin +ve |
| Molecular | ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene |
| Site | salivary gland - usually parotid |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Clin. DDx | other salivary gland tumours |
Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma, abbreviated MASC, is a newly described malignant salivary gland tumour.[1]
General
- Microscopic appearance similar to secretory breast carcinoma.[2]
- Super rare - 21 cases in the world literature as of 2012.[1]
- Original paper described it only in adults.[2]
- Has been described in a pediatric patient.[3]
Gross
- Usually parotid gland.[2]
- Well-circumscribed.[citation needed]
Microscopic
Features:
- Large cells with abundant cytoplasm.
- Small nuclei.
- +/-Lymphocytic infiltrate.
- Solid and microcystic growth pattern.
DDx:
- Acinic cell carcinoma - very closely mimics.
- Abundant basophilic granular cytoplasm.[1]
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
Images
Stains
Features:[2]
- PAS stain +ve.
- Mucicarmine stain +ve.
IHC
Features:[2]
- S-100 +ve.[1]
- Mammomglobin +ve.
- Vimentin +ve.
Others:
- p63 -ve.
- HMWCK -ve.
- GATA3 +ve.
Panel:
- S-100, mammoglobin, p63, HMWCK.
Molecular
- t(12;15)(p13;q25).
- Fusion of the genes ETV6 and NTRK3.[1]
Note:
- The translocation seen in secretory breast carcinoma and congenital-infantile fibrosarcoma.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Lei, Y.; Chiosea, SI. (Jun 2012). "Re-evaluating historic cohort of salivary acinic cell carcinoma with new diagnostic tools.". Head Neck Pathol 6 (2): 166-70. doi:10.1007/s12105-011-0312-9. PMID 22127547.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Skálová, A.; Vanecek, T.; Sima, R.; Laco, J.; Weinreb, I.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Starek, I.; Geierova, M. et al. (May 2010). "Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary glands, containing the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene: a hitherto undescribed salivary gland tumor entity.". Am J Surg Pathol 34 (5): 599-608. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181d9efcc. PMID 20410810.
- ↑ Rastatter, JC.; Jatana, KR.; Jennings, LJ.; Melin-Aldana, H. (Mar 2012). "Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of the parotid gland in a pediatric patient.". Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146 (3): 514-5. doi:10.1177/0194599811419044. PMID 21873597.