Difference between revisions of "Ganglion cyst"
(→Gross) |
|||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
*Classically on the wrist.<ref name=pmid17488856>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hasham | first1 = S. | last2 = Burke | first2 = FD. | title = Diagnosis and treatment of swellings in the hand. | journal = Postgrad Med J | volume = 83 | issue = 979 | pages = 296-300 | month = May | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1136/pgmj.2005.043992 | PMID = 17488856 }}</ref> | *Classically on the wrist.<ref name=pmid17488856>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hasham | first1 = S. | last2 = Burke | first2 = FD. | title = Diagnosis and treatment of swellings in the hand. | journal = Postgrad Med J | volume = 83 | issue = 979 | pages = 296-300 | month = May | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1136/pgmj.2005.043992 | PMID = 17488856 }}</ref> | ||
*May be painful.<ref name=Ref_Derm322>{{Ref Derm|322}}</ref> | *May be painful.<ref name=Ref_Derm322>{{Ref Derm|322}}</ref> | ||
*Many (~60%) regress if left alone.<ref name=pmid24967120>{{Cite journal | last1 = Suen | first1 = M. | last2 = Fung | first2 = B. | last3 = Lung | first3 = CP. | title = Treatment of ganglion cysts. | journal = ISRN Orthop | volume = 2013 | issue = | pages = 940615 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1155/2013/940615 | PMID = 24967120 }}</ref> | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 16 September 2015
| Ganglion cyst | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
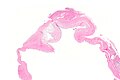
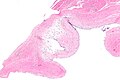
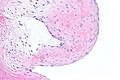
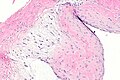
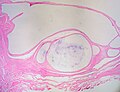
 Ganglion cyst. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | empty space(s) - usually multiple; fibrotic wall without an epithelial lining +/- myxoid change +/- spindled fibroblasts |
| LM DDx | synovial cyst, juxta-articular myxoma, (other) myxomas, digital mucous cyst |
| Site | soft tissue close to joints - esp. in hand |
|
| |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
Ganglion cyst is a small benign ditzel classically found on the wrist.
General
- Very common.
- Most common tumour of the hand.[1]
- Classically on the wrist.[2]
- May be painful.[3]
- Many (~60%) regress if left alone.[4]
Gross
- Mass at a joint - classically in the hand.
DDx - clinical:
- Metacarpal boss - degenerative arthritis.[5]
- Giant cell tumour of tendon sheath.
Image
Microscopic
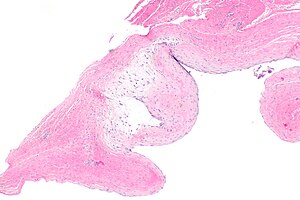
- Empty space(s); usually multiple.
- Fibrotic wall.
- No epithelial lining.†
- +/-Myxoid change - very common.
- May have some spindled fibroblasts.
† The entity is really a pseudocyst.[1]
DDx:
- Synovial cyst - true cyst (has an epithelial lining), villous projections into the cystic space.
- Juxta-articular myxoma.
- Myxoma.
- Digital mucous cyst - has many spindled fibroblasts, usu. superficial.[3]
Images
www:
Sign out
SOFT TISSUE ("GANGLION CYST"), LEFT WRIST, EXCISION:
- GANGLION CYST.
Micro
The sections show fibroadipose tissue with cyst-like spaces surrounded by fibrous tissue. There are no villous projections into the cyst-like spaces. Focal myxoid areas are present with rare bland spindle cells. There is no nuclear atypia and no mitotic activity is appreciated. Dense connective tissue consistent with tendon is present focally.
Alternate
The sections show cyst-like spaces surrounded by fibrous tissue. There are no villous projections into the cyst-like spaces. Focal myxoid areas are present with rare bland spindle cells. There is no nuclear atypia and no mitotic activity is appreciated. Dense connective tissue consistent with tendon is present focally. Benign glands are present.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1253223-overview]. Accessed on: 8 February 2012. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "emed_gc" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Hasham, S.; Burke, FD. (May 2007). "Diagnosis and treatment of swellings in the hand.". Postgrad Med J 83 (979): 296-300. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2005.043992. PMID 17488856.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 322. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Suen, M.; Fung, B.; Lung, CP. (2013). "Treatment of ganglion cysts.". ISRN Orthop 2013: 940615. doi:10.1155/2013/940615. PMID 24967120.
- ↑ Cuono, CB.; Watson, HK. (Jan 1979). "The carpal boss: surgical treatment and etiological considerations.". Plast Reconstr Surg 63 (1): 88-93. PMID 432327.