Difference between revisions of "Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+images) |
m (touch) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
| Image = Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder -- intermed mag.jpg | | Image = Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder -- intermed mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
Revision as of 08:07, 13 April 2015
| Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
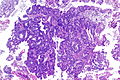
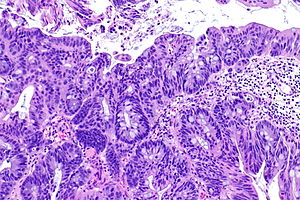 Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder |
|
| |
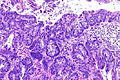
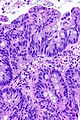
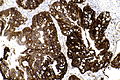
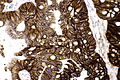
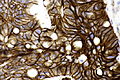
| LM | nuclear pleomorphism (may be mild), usually glandular differentiation (most common), no urothelial differentiation - essential |
| LM DDx | urachal carcinoma, invasive urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation, metastatic adenocarcinoma (esp. colorectal adenocarcinoma) |
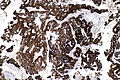
| IHC | CK7 +ve, CK20 +ve, CDX2 +ve (strong, diffuse), beta-catenin +ve (membranous, not nuclear) |
| Grossing notes | radical cystectomy grossing, cystoprostatectomy grossing |
| Site | urinary bladder |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Treatment | cystectomy |
Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder, also primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder and bladder adenocarcinoma, is a very uncommon malignant urinary bladder tumour.
General
Clinical:
- Like urothelial carcinoma - usually hematuria.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Nuclear pleomorphism - may be mild.
- Usually glandular differentiation (most common).
- Frequently looks just like colorectal adenocarcinoma.
- Without urothelial differentiation - essential.[3]
Subtypes:[2]
- Glandular.
- Papillary.
- Colloidal (mucinous).
- Signet ring cell carcinoma.
- Clear cell carcinoma (also mesonephroid carcinoma).
DDx:
- Urachal carcinoma - dome of bladder.
- Invasive urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation - has urothelial differentiation.
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma.
Images
Case 1
IHC
Features - variable:[4]
- CK7 +ve.
- CK20 +ve.
- CDX2 +ve (strong, diffuse).
- Beta-catenin +ve (membranous, not nuclear).
- Colorectal adenocarcinoma typically has nuclear staining and membranous staining.
- Thrombomodulin +ve/-ve (~60% of cases).
- Colorectal adenocarcinoma -ve.
- Urothelial carcinoma +ve (~90% of cases).
Images
Case 1
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ranadive, NU.; Trivedi, VD.; Gadgil, NM. (Oct 1999). "Primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder: a study of 6 cases from the pathologist's point of view.". Arch Esp Urol 52 (8): 906-11. PMID 11762445.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Abbas, M.; Kramer, MW.; Wolters, M.; Herrman, TR.; Becker, JU.; Kreipe, HH. (Feb 2013). "Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder, mesonephroid type: a rare case.". Rare Tumors 5 (1): e3. doi:10.4081/rt.2013.e3. PMID 23772302.
- ↑ Zhong, M.; Gersbach, E.; Rohan, SM.; Yang, XJ. (Mar 2013). "Primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder: differential diagnosis and clinical relevance.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 137 (3): 371-81. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0076-RA. PMID 23451748.
- ↑ Roy, S.; Parwani, AV. (Dec 2011). "Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 135 (12): 1601-5. doi:10.5858/arpa.2009-0713-RS. PMID 22129192.