Difference between revisions of "Epidermal necrosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→General: more) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
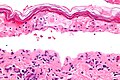
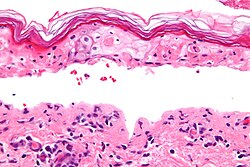
[[Image:Confluent_epidermal_necrosis_-_very_high_mag.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Confluent epidermal necrosis. [[H&E stain]].]] | |||
'''Epidermal necrosis''' is an important finding in [[dermatopathology]]. Full-thickness necrosis, especially is very serious. | '''Epidermal necrosis''' is an important finding in [[dermatopathology]]. Full-thickness necrosis, especially is very serious. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
**These are signed-out as "confluent epidermal necrosis - see comment". | **These are signed-out as "confluent epidermal necrosis - see comment". | ||
***Comment: The histomorphologic findings are consistent with EM/SJS/TEN. | ***Comment: The histomorphologic findings are consistent with EM/SJS/TEN. | ||
**The clinical DDx of EM/SJS/TEN includes ''[[acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis]]'' (AGEP). | |||
==Erythema multiforme== | ==Erythema multiforme== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1189>{{Ref PBoD8|1189}}</ref> | Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1189>{{Ref PBoD8|1189}}</ref> | ||
*Hypersensitivity disorder due to a drug ''or'' infection. | *[[Hypersensitivity]] disorder due to a drug ''or'' infection. | ||
**Associated with the following: [[HSV]], Mycoplasma, [[Histoplasma]], others. | **Associated with the following: [[HSV]], Mycoplasma, [[Histoplasma]], others. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 37: | ||
*+/-Epidermal blistering. | *+/-Epidermal blistering. | ||
*+/-Epidermal sloughing. | *+/-Epidermal sloughing. | ||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
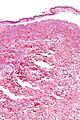
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - low mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - low mag. (WC) | |||
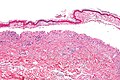
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - intermed mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
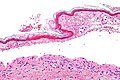
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - high mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - very high mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Stevens-Johnson syndrome== | ==Stevens-Johnson syndrome== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 50: | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
Rx causes of SJS: | Rx causes of SJS: | ||
* | *[[NSAID]]s. | ||
*Anticonvulsants. | *Anticonvulsants. | ||
*Sulfonamides. | *Sulfonamides. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 58: | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Similar [[erythema multiforme]]. | *Similar [[erythema multiforme]]. | ||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - low mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - intermed mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - high mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - very high mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Toxic epidermal necrolysis== | ==Toxic epidermal necrolysis== | ||
| Line 61: | Line 79: | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Like [[erythema multiforme]] - but usu. less inflammation.<ref>S. Sade. 8 September 2011.</ref> | *Like [[erythema multiforme]] - but usu. less inflammation.<ref>S. Sade. 8 September 2011.</ref> | ||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - low mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - intermed mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - high mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image: Confluent epidermal necrosis - very high mag.jpg | Confluent epidermal necrosis - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome== | ==Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome== | ||
*Abbreviated ''SSSS''. | *Abbreviated ''SSSS''. | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *Due to keratinocyte cell-cell adhesion loss in the superficial epidermis - caused by ''S. aureus''.<ref name=pmid17582744>{{Cite journal | last1 = Nishifuji | first1 = K. | last2 = Sugai | first2 = M. | last3 = Amagai | first3 = M. | title = Staphylococcal exfoliative toxins: "molecular scissors" of bacteria that attack the cutaneous defense barrier in mammals. | journal = J Dermatol Sci | volume = 49 | issue = 1 | pages = 21-31 | month = Jan | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.05.007 | PMID = 17582744 }}</ref> | ||
Clinical: | Clinical: | ||
*Blisters | *Blisters | ||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features:<ref name=pmid17582744/> | Features:<ref name=pmid17582744/> | ||
* | *Superficial dermis separates from underlying tissue - looks artefactual. | ||
*Minimal/scant inflammation is typical.<ref>URL: [http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/display.cfm?ImageID=2105774586 http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/display.cfm?ImageID=2105774586]. Accessed on: 22 September 2011.</ref> | |||
Image: | |||
*[http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/display.cfm?ImageID=2105774586 SSSS (jhmi.edu)]. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Dermatopathology]] - an introduction to the topic. | *[[Dermatopathology]] - an introduction to the topic. | ||
*[[Non-malignant skin disease]]. | *[[Non-malignant skin disease]]. | ||
*[[Inflammatory skin disease]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 05:47, 9 November 2014

Confluent epidermal necrosis. H&E stain.
Epidermal necrosis is an important finding in dermatopathology. Full-thickness necrosis, especially is very serious.
General
Full thickness DDx:
- Erythema multiform (EM).
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS).
- Trauma.
- Others. (???)
Partial thickness DDx:
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome.
- Trauma. (???)
- Others. (???)
Notes:
- SJS and TEN are on a spectrum, EM (depending on who you ask) is considered separate.
- These are signed-out as "confluent epidermal necrosis - see comment".
- Comment: The histomorphologic findings are consistent with EM/SJS/TEN.
- The clinical DDx of EM/SJS/TEN includes acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP).
- These are signed-out as "confluent epidermal necrosis - see comment".
Erythema multiforme
- Abbreviated EM.
General
Features:[1]
- Hypersensitivity disorder due to a drug or infection.
- Associated with the following: HSV, Mycoplasma, Histoplasma, others.
Clinical:
- Target-like lesion.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Lymphocytic interface dermatitis (lymphocytes at the dermal-epidermal junction).
- Necrotic/degenerative keratinocytes - key feature.
- +/-Epidermal blistering.
- +/-Epidermal sloughing.
Images
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Abbreviated SJS.
General
Rx causes of SJS:
- NSAIDs.
- Anticonvulsants.
- Sulfonamides.
- Penicillins.
Microscopic
Features:
- Similar erythema multiforme.
Images
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Abbreviated TEN.
General
- TEN more severe form SJS.
Definition:
- >30% sheet-like epidermal detachment, diffuse erythema, severe mucous membrane involvement.
- Most TEN (80%) Rx-related, only 50% of SJS Rx-related.
Microscopic
Features:
- Like erythema multiforme - but usu. less inflammation.[2]
Images
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
- Abbreviated SSSS.
General
- Due to keratinocyte cell-cell adhesion loss in the superficial epidermis - caused by S. aureus.[3]
Clinical:
- Blisters
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Superficial dermis separates from underlying tissue - looks artefactual.
- Minimal/scant inflammation is typical.[4]
Image:
See also
- Dermatopathology - an introduction to the topic.
- Non-malignant skin disease.
- Inflammatory skin disease.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1189. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ S. Sade. 8 September 2011.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Nishifuji, K.; Sugai, M.; Amagai, M. (Jan 2008). "Staphylococcal exfoliative toxins: "molecular scissors" of bacteria that attack the cutaneous defense barrier in mammals.". J Dermatol Sci 49 (1): 21-31. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.05.007. PMID 17582744.
- ↑ URL: http://dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu/derm/display.cfm?ImageID=2105774586. Accessed on: 22 September 2011.