Difference between revisions of "Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split-out) |
(tweak) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Storiform_pattern_-_very_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = DFSP. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Micro = dermal spindle cell lesion with storiform pattern, typically contains adipose tissue within the tumour -- described as "honeycomb pattern" and "Swiss cheese pattern" | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[dermatofibroma]], [[dermatomyofibroma]], [[nodular fasciitis]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = CD34 +ve, Factor XIIIa -ve | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = t(17;22)(q22;q15) | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = firm plaque +/-ulceration | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[skin]] - usually trunk or proximal extremities | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = second to fifth decade | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = moderate, locally aggressive, rarely metastases | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = wide excision | |||
}} | |||
'''Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans''', abbreviated '''DFSP''', is a rare locally aggressive [[dermatologic neoplasms|tumour of the skin]]. | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Destroys adnexal structures - somewhat unusual for a mostly benign tumour. | |||
*Destroys adnexal structures. | |||
*Occasionally transforms to a (more aggressive) [[adult fibrosarcoma|fibrosarcoma]].<ref name=pmid21128251>{{Cite journal | last1 = Stacchiotti | first1 = S. | last2 = Pedeutour | first2 = F. | last3 = Negri | first3 = T. | last4 = Conca | first4 = E. | last5 = Marrari | first5 = A. | last6 = Palassini | first6 = E. | last7 = Collini | first7 = P. | last8 = Keslair | first8 = F. | last9 = Morosi | first9 = C. | title = Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans-derived fibrosarcoma: clinical history, biological profile and sensitivity to imatinib. | journal = Int J Cancer | volume = 129 | issue = 7 | pages = 1761-72 | month = Oct | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1002/ijc.25826 | PMID = 21128251 }}</ref> | *Occasionally transforms to a (more aggressive) [[adult fibrosarcoma|fibrosarcoma]].<ref name=pmid21128251>{{Cite journal | last1 = Stacchiotti | first1 = S. | last2 = Pedeutour | first2 = F. | last3 = Negri | first3 = T. | last4 = Conca | first4 = E. | last5 = Marrari | first5 = A. | last6 = Palassini | first6 = E. | last7 = Collini | first7 = P. | last8 = Keslair | first8 = F. | last9 = Morosi | first9 = C. | title = Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans-derived fibrosarcoma: clinical history, biological profile and sensitivity to imatinib. | journal = Int J Cancer | volume = 129 | issue = 7 | pages = 1761-72 | month = Oct | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1002/ijc.25826 | PMID = 21128251 }}</ref> | ||
*Typically slow growing.<ref name=pmid23327727>{{Cite journal | last1 = Llombart | first1 = B. | last2 = Serra-Guillén | first2 = C. | last3 = Monteagudo | first3 = C. | last4 = López Guerrero | first4 = JA. | last5 = Sanmartín | first5 = O. | title = Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a comprehensive review and update on diagnosis and management. | journal = Semin Diagn Pathol | volume = 30 | issue = 1 | pages = 13-28 | month = Feb | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1053/j.semdp.2012.01.002 | PMID = 23327727 }}</ref> | |||
*Usually second to fifth decade.<ref name=pmid23327727/> | |||
Treatment:<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1183>{{Ref PBoD8|1183}}</ref> | Treatment:<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1183>{{Ref PBoD8|1183}}</ref> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 60: | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*Adnexal structure within tumour are preserved -- this is unusual for a malignant tumour -- '''important'''. | *Adnexal structure within tumour are preserved -- this is unusual for a malignant tumour -- '''important'''. | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
| Line 41: | Line 71: | ||
*[[Solitary fibrous tumour]]. | *[[Solitary fibrous tumour]]. | ||
*[[Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma]]. | *[[Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma]]. | ||
===Subtypes=== | |||
Numerous variants/subtypes are described:<ref name=pmid23327727>{{Cite journal | last1 = Llombart | first1 = B. | last2 = Serra-Guillén | first2 = C. | last3 = Monteagudo | first3 = C. | last4 = López Guerrero | first4 = JA. | last5 = Sanmartín | first5 = O. | title = Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a comprehensive review and update on diagnosis and management. | journal = Semin Diagn Pathol | volume = 30 | issue = 1 | pages = 13-28 | month = Feb | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1053/j.semdp.2012.01.002 | PMID = 23327727 }}</ref> | |||
*Pigmented DFSP (Bednar tumour). | |||
*Myxoid DFSP. | |||
*Myoid DFSP. | |||
*Granular cell DFSP. | |||
*Sclerotic DFSP. | |||
*Atrophic DFSP, | |||
*Giant cell fibroblastoma. | |||
*DFSP with fibrosarcomatous areas. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 99: | ||
*Factor XIIIa -ve. | *Factor XIIIa -ve. | ||
**Usually positive in dermatofibroma.<ref name=pmid7694515>{{cite journal |author=Abenoza P, Lillemoe T |title=CD34 and factor XIIIa in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans |journal=Am J Dermatopathol |volume=15 |issue=5 |pages=429–34 |year=1993 |month=October |pmid=7694515 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid9129699>{{cite journal |author=Goldblum JR, Tuthill RJ |title=CD34 and factor-XIIIa immunoreactivity in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and dermatofibroma |journal=Am J Dermatopathol |volume=19 |issue=2 |pages=147–53 |year=1997 |month=April |pmid=9129699 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | **Usually positive in dermatofibroma.<ref name=pmid7694515>{{cite journal |author=Abenoza P, Lillemoe T |title=CD34 and factor XIIIa in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans |journal=Am J Dermatopathol |volume=15 |issue=5 |pages=429–34 |year=1993 |month=October |pmid=7694515 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid9129699>{{cite journal |author=Goldblum JR, Tuthill RJ |title=CD34 and factor-XIIIa immunoreactivity in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and dermatofibroma |journal=Am J Dermatopathol |volume=19 |issue=2 |pages=147–53 |year=1997 |month=April |pmid=9129699 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* | *S-100 -ve (screen for melanoma). | ||
*Caldesmin -ve (screen for muscle differentiation). | *Caldesmin -ve (screen for muscle differentiation). | ||
*Beta-catenin. (???) | *Beta-catenin. (???) | ||
| Line 70: | Line 111: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Dermatologic neoplasms]]. | *[[Dermatologic neoplasms]]. | ||
*[[Dermatofibroma]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 11:35, 21 June 2014
| Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
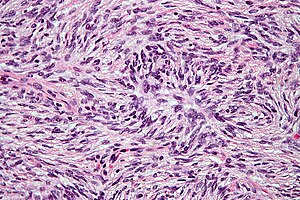 DFSP. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | dermal spindle cell lesion with storiform pattern, typically contains adipose tissue within the tumour -- described as "honeycomb pattern" and "Swiss cheese pattern" |
| LM DDx | dermatofibroma, dermatomyofibroma, nodular fasciitis |
| IHC | CD34 +ve, Factor XIIIa -ve |
| Molecular | t(17;22)(q22;q15) |
| Gross | firm plaque +/-ulceration |
| Site | skin - usually trunk or proximal extremities |
|
| |
| Clinical history | second to fifth decade |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | moderate, locally aggressive, rarely metastases |
| Treatment | wide excision |
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, abbreviated DFSP, is a rare locally aggressive tumour of the skin.
General
- Destroys adnexal structures - somewhat unusual for a mostly benign tumour.
- Occasionally transforms to a (more aggressive) fibrosarcoma.[1]
- Typically slow growing.[2]
- Usually second to fifth decade.[2]
Treatment:[3]
- Wide excision.
- May include imatinib (Gleevec).
Gross
Features:[4]
- Firm plaque, often bosselated, usually on the trunk.
- +/-Ulceration.
Images:
- Protuberant DFSP (dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu).
- Huge DFSP on back (dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu).
- Protuberant DFSP - gross and histology (dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu).
Microscopic
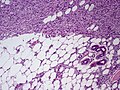
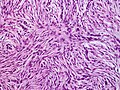
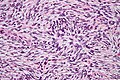
Features:[3]
- Dermal spindle cell lesion with storiform pattern.
- Spokes of the wheel-pattern.
- Contains adipose tissue within the tumour -- key feature.
- Described as "honeycomb pattern" and "Swiss cheese pattern".
Notes:
- Adnexal structure within tumour are preserved -- this is unusual for a malignant tumour -- important.
DDx:
- Dermatofibroma - main DDx - has entrapment of collagen bundles at the edge of the lesion.
- Dermatomyofibroma.[5]
- Nodular fasciitis.
DDx of storiform pattern:
- DFSP.
- Dermatofibroma.
- Solitary fibrous tumour.
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma.
Subtypes
Numerous variants/subtypes are described:[2]
- Pigmented DFSP (Bednar tumour).
- Myxoid DFSP.
- Myoid DFSP.
- Granular cell DFSP.
- Sclerotic DFSP.
- Atrophic DFSP,
- Giant cell fibroblastoma.
- DFSP with fibrosarcomatous areas.
Images
www:
IHC
Panel:[6]
- CD34 +ve.
- Factor XIIIa -ve.
- S-100 -ve (screen for melanoma).
- Caldesmin -ve (screen for muscle differentiation).
- Beta-catenin. (???)
- MIB1 (proliferation marker).
- Should not be confused with MIB-1 a gene that regulates apoptosis.
Molecular
A characteristic translocation is seen:[9] t(17;22)(q22;q15) COLA1/PDGFB.
See also
References
- ↑ Stacchiotti, S.; Pedeutour, F.; Negri, T.; Conca, E.; Marrari, A.; Palassini, E.; Collini, P.; Keslair, F. et al. (Oct 2011). "Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans-derived fibrosarcoma: clinical history, biological profile and sensitivity to imatinib.". Int J Cancer 129 (7): 1761-72. doi:10.1002/ijc.25826. PMID 21128251.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Llombart, B.; Serra-Guillén, C.; Monteagudo, C.; López Guerrero, JA.; Sanmartín, O. (Feb 2013). "Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a comprehensive review and update on diagnosis and management.". Semin Diagn Pathol 30 (1): 13-28. doi:10.1053/j.semdp.2012.01.002. PMID 23327727.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1183. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 600. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 504. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ AP. May 2009.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Abenoza P, Lillemoe T (October 1993). "CD34 and factor XIIIa in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans". Am J Dermatopathol 15 (5): 429–34. PMID 7694515.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Goldblum JR, Tuthill RJ (April 1997). "CD34 and factor-XIIIa immunoreactivity in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and dermatofibroma". Am J Dermatopathol 19 (2): 147–53. PMID 9129699.
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1249. ISBN 978-1416031215.