Difference between revisions of "Dermal scar"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split out) |
(more) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = ScarHistology.JPG | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Dermal scar. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Micro = dense collagen - fibers run parallel to the DE junction, loss of dermal papilla, loss of adnexal structures, thin-wall blood vessels | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[malignant melanoma]] desmoplastic-neurotropic type, [[dermatofibroma]], desmoplastic [[Spitz nevus]], sclerosing [[blue nevus]] | |||
| Stains = S-100 -ve (mostly) | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[skin]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = trauma, previous excision or biopsy | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = common | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
}} | |||
{{ Infobox external links | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| EHVSC = | |||
| EHVSC_mult = {{EHVSC3|10187|Dermal scar adjacent to a basal cell carcinoma}} | |||
| pathprotocols = | |||
| wikipedia = Scar | |||
| pathoutlines = | |||
}} | |||
'''Dermal scar''', also simply '''scar''', is commonly seen in [[dermatopathology]]. It is also known a '''cicatrix'''. | '''Dermal scar''', also simply '''scar''', is commonly seen in [[dermatopathology]]. It is also known a '''cicatrix'''. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 64: | ||
Image:ScarHistology.JPG | Scar. (WC) | Image:ScarHistology.JPG | Scar. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
*S100 focal/scattered +ve. | *S100 focal/scattered +ve. | ||
| Line 46: | Line 84: | ||
*[[Non-malignant skin disease]]. | *[[Non-malignant skin disease]]. | ||
*[[Dermatopathology]]. | *[[Dermatopathology]]. | ||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Dermatopathology]] | [[Category:Dermatopathology]] | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 3 August 2013
| Dermal scar | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
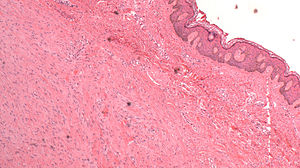 Dermal scar. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | dense collagen - fibers run parallel to the DE junction, loss of dermal papilla, loss of adnexal structures, thin-wall blood vessels |
| LM DDx | malignant melanoma desmoplastic-neurotropic type, dermatofibroma, desmoplastic Spitz nevus, sclerosing blue nevus |
| Stains | S-100 -ve (mostly) |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Clinical history | trauma, previous excision or biopsy |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Dermal scar | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| EHVSC | 10187 (Dermal scar adjacent to a basal cell carcinoma) |
| Wikipedia | Scar |
Dermal scar, also simply scar, is commonly seen in dermatopathology. It is also known a cicatrix.
General
- Previous surgery, biopsy, trauma.
Microscopic
Features:
- Loss of dermal papilla.
- Dense collagen - fibers run parallel to the dermal-epidermal (DE) junction[1] - key feature.
- Loss of adnexal structures.
Other feature:
- Thin-walled blood vessels.
- Described as running perpendicular to the surface[1] - this may not be apparent.
Note:
- There should not be any nuclear hyperchromasia or pleomorphism.[2]
DDx:
- Malignant melanoma, desmoplastic-neurotropic type - nuclear pleomorphism and/or hyperchromasia; may be focal.[2]
- Dermatofibroma.
- Desmoplastic Spitz nevus.
- Sclerosing blue nevus.
Image
IHC
- S100 focal/scattered +ve.
- Desmoplastic melanoma strong +ve.
- HMB-45 -ve.
- Sclerosing blue nevus +ve.
Sign out
SKIN, LOWER MID BACK, RE-EXCISION: - DERMAL SCAR. - SOLAR ELASTOSIS.
Micro
The sections show skin with a dermis with dense collagen fibres that run parallel to the skin surface without adnexal structures. The overlying dermal-epidermis interface lacks the typical undulation.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 499. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 479. ISBN 978-0443066542.