Difference between revisions of "Pilomatricoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Sign out: fix) |
(+| Clinicalhx =) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Syndromes = | | Syndromes = | ||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = hard nodule | | Signs = hard nodule | ||
| Symptoms = +/-painful | | Symptoms = +/-painful | ||
Revision as of 20:46, 5 July 2013
| Pilomatricoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
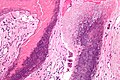
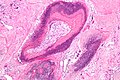
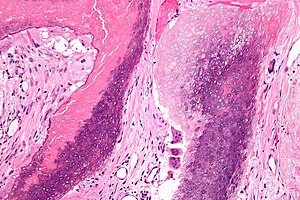 Pilomatricoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | "ghost" cells, foreign body-type giant cells |
| LM DDx | squamous cell carcinoma, pilomatrix carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, epidermal inclusion cyst |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Signs | hard nodule |
| Symptoms | +/-painful |
| Prognosis | benign |
Pilomatricoma is a benign skin lesion that is common in childhood. It may be spelled pilomatrixoma.
It is also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe.[1]
General
- Benign skin tumour.
- Most common solid skin tumour of children.[2]
- CTNNB1 gene mutation important in pathogenesis.[3]
Clinical:
- Hard nodule - calcification.
- +/-Painful.
Treatment:
- Surgical excision.[2]
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Nodular circumscribed lower dermis/subcutaneous adipose lesion; thus, usu. surrounded by connective tissue.
- Sharpy demarcated island of cells.
- Calcification in 75%.
- Cells:[5]
- Basaloid epithelial cells - have prominent nucleoli.
- Anucleate squamous cells ("ghost cells").
- Giant cell foreign body type granulomas (form in reaction to keratin).
Notes:
- Keratin a prominent feature on cytology - lots of orange stuff.
- May ossify.
DDx:
- Epidermal inclusion cyst.
- Pilomatrix carcinoma - invasive border, cytologic atypia, necrosis.[6]
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
- Basal cell carcinoma.
Images
www:
Sign out
SKIN LESION, RIGHT ARM, EXCISION: - PILOMATRICOMA.
See also
References
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 387. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058965-overview. Accessed on: 10 September 2011. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "emed1058965" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 597. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1058965-diagnosis. Accessed on: 10 September 2011.
- ↑ http://www.bccancer.bc.ca/HPI/CE/cytotechnology/cytosleuthquiz/nongyne/ngcase02d.htm
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 389. ISBN 978-0443066542.