Difference between revisions of "Rosai-Dorfman disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Tag: Mobile edit |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Rosai-Dorfman disease. H&E stain. | | Caption = Rosai-Dorfman disease. H&E stain. | ||
| Micro = | | Micro = sinus histiocytosis - histiocytes have a singular large round nucleus with a prominent nucleolus (visible with 10x objective); emperipolesis | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = | | LMDDx = | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Sinus histiocytosis]]. | |||
*Other histiocytosis: | *Other histiocytosis: | ||
**[[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]]. | **[[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]]. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 64: | ||
Image:Emperipolesis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Emperipolesis in SHML (WC) | Image:Emperipolesis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Emperipolesis in SHML (WC) | ||
Image:Rosai-Dorfman_disease_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Rosai-Dorfman disease (WC) | Image:Rosai-Dorfman_disease_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Rosai-Dorfman disease (WC) | ||
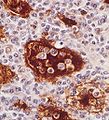
Image:Rosai-dorfman.jpg | Rosai-Dorfman disease - | Image:Rosai-dorfman.jpg | Rosai-Dorfman disease - S-100 showing emperipolesis (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
www: | www: | ||
| Line 73: | Line 74: | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
*CD68 +ve. | *CD68 +ve. | ||
* | *S-100 +ve. | ||
**Useful for seeing emperipolesis. | **Useful for seeing emperipolesis. | ||
*CD1a -ve. | *CD1a -ve. | ||
**CD1a | **CD1a +ve in [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]]. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 15:44, 1 December 2013
| Rosai-Dorfman disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
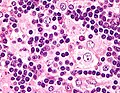
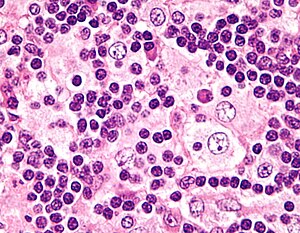 Rosai-Dorfman disease. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | sinus histiocytosis - histiocytes have a singular large round nucleus with a prominent nucleolus (visible with 10x objective); emperipolesis |
| IHC | CD68 -ve, S-100 +ve, CD1a -ve |
| Site | lymph nodes - see lymph node pathology |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
Rosai-Dorfman disease, abbreviated RDD, is a rare lymph node pathology.
It is also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy,[1] abbreviated SHML.
General
- Super rare.
- Prognosis - good.
Clinical findings:[2]
- Fever.
- Leukocytosis with neutrophilia.
- Polyclonal gammaglobulinemia.
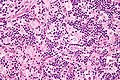
Microscopic
Features:
- Sinus histiocytosis:
- Histiocytes - abundant.
- Singular large round nuclei[3] ~2x the size of resting lymphocyte.
- Prominent nucleolus - visible with 10x objective.
- Abundant cytoplasm.
- Singular large round nuclei[3] ~2x the size of resting lymphocyte.
- Histiocytes - abundant.
- Emperipolesis (from Greek: em = inside, peri = around, polemai = wander about[4]):
DDx:
- Sinus histiocytosis.
- Other histiocytosis:
- Infection, e.g. rhinoscleroma (nasopharynx), xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis.
- Xanthomatous change.
Images
www:
- RDD - case 1 - several images (upmc.edu).
- RDD - case 2 - several images of breast (upmc.edu).
- RDD - case 3 - several images (upmc.edu).
- RDD - case 4 - several images (upmc.edu).
IHC
- CD68 +ve.
- S-100 +ve.
- Useful for seeing emperipolesis.
- CD1a -ve.
- CD1a +ve in Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
See also
References
- ↑ Agarwal A, Pathak S, Gujral S (October 2006). "Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy--a review of seven cases". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 49 (4): 509–15. PMID 17183839.
- ↑ Landim, FM.; Rios, Hde O.; Costa, CO.; Feitosa, RG.; Rocha Filho, FD.; Costa, AA. (Jul 2009). "Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease.". An Bras Dermatol 84 (3): 275-8. PMID 19668942.
- ↑ Bailey, D. 24 August 2010.
- ↑ Stedman's Medical Dictionary. 27th Ed.
- ↑ Viswanathan P, Raghunathan K, Majhi U, Pandit RV, Shanthi R, Rajkumar T (1997). Emperipolesis : an electron microscopic characteristic in RDD (Rosai-Dorfaman disease) : a case report. pp. 14-6. http://www.ijmpo.org/article.asp?issn=0971-5851;year=1997;volume=18;issue=1;spage=14;epage=16;aulast=Viswanathan;type=0.
- ↑ Lyons DJ, Gautam A, Clark J, et al. (January 1992). "Lymphocyte macrophage interactions: peripolesis of human alveolar macrophages". Eur. Respir. J. 5 (1): 59–66. PMID 1577151.