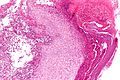
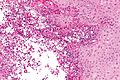
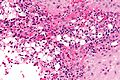
Rhinoscleroma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
| Rhinoscleroma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
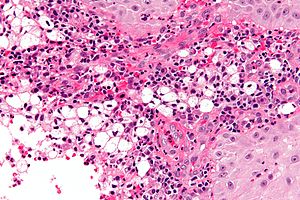 Rhinoscleroma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | macrophages with clear-to-foamy cytoplasm, lymphocytes, plasma cells |
| LM DDx | Rosai-Dorfman disease |
| Stains | Warthin-Starry stain +ve (rod-shaped organisms) |
| IHC | CD68 +ve, S100 -ve |
| Site | head and neck - usu. nose |
|
| |
| Signs | nasal deformation (late) |
| Prevalence | rare |
Rhinoscleroma is a rare infectious condition of the head and neck.
General
- Caused by Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis.
- Nose involved +95% of the time.[1]
Gross
- Nasal mass - may be deforming.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Macrophages - clear-to-foamy cytoplasm.
- Lymphocytes.
- Plasma cells.
DDx:
- Rosai-Dorfman disease - usu. has emperipolesis.[3]
Images
www:
Stains
- Warthin-Starry stain +ve (rod-shaped organisms).
- Dieterle stain +ve (rod-shaped organisms).
IHC
- S100 -ve.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Chan, TV.; Spiegel, JH. (Oct 2007). "Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis of the membranous nasal septum.". J Laryngol Otol 121 (10): 998-1002. doi:10.1017/S0022215107006421. PMID 17359555.
- ↑ URL: http://www.brown.edu/Courses/Digital_Path/systemic_path/hn/rhinoscleroma2.html. Accessed on: 18 January 2012.
- ↑ Iyer VK, Handa KK, Sharma MC (July 2009). "Variable extent of emperipolesis in the evolution of Rosai Dorfman disease: Diagnostic and pathogenetic implications". J Cytol 26 (3): 111–6. doi:10.4103/0970-9371.59398. PMC 3168012. PMID 21938169. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3168012/.
- ↑ URL: http://www.jameswpattersonmd.com/case_studies/index.cfm?CFID=387434. Accessed on: 21 February 2012.
- ↑ Ilie M, Guevara N, Castillo L, Hofman P (March 2010). "Polypoid intranasal mass caused by Rosai-Dorfman disease: a diagnostic pitfall". J Laryngol Otol 124 (3): 345–8. doi:10.1017/S0022215109990818. PMID 19646302.