Radiation changes
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
| Radiation changes | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
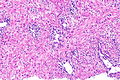
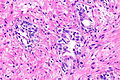
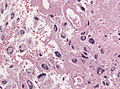
 Radiation changes. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | cytoplasmic vacuolation (usually abundant), enlarged nuclei - but usu. normal NC ratio, no nuclear membrane irregularies, chromatin "smudgy", +/-multinucleation, +/-fibrosis (chronic change), +/-edema (acute change) |
| LM DDx | pleomorphic tumours - esp. sarcomas, poorly differentiated carcinomas, drug/toxin effect, well-differentiated tumours in the background of radiation changes, "giant cell cystitis" |
| IHC | Ki-67 low, pankeratin -ve (usu.) |
| Site | pretty much anywhere |
|
| |
| Clinical history | history of radiation treatment/exposure - important for the diagnosis |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | cancer recurrence, infection, new malignancy, post-surgical changes |
Radiation changes, also radiation effects, are seen occasionally by pathologists. They are usually a result of prior (radiation) treatments. The history is important in making this diagnosis.
General
- History of radiation treatment/exposure.
- Clinical symptoms dependent on site.
Gross
- +/-Erythema (early)
- +/-Fibrotic appearing tissue (late).
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Cytoplasmic vacuolation - usually abundant.
- Nucleus:
- Enlarged nucleus - but normal NC ratio.
- No nuclear membrane irregularies.
- Chromatin: "smudgy".
- +/-Multinucleation.
- +/-Fibrosis (chronic change).
- +/-Edema (acute change).
Important note:
- The atypical cells are stromal cells; these survive the radiation. The epithelium is usually normal in the context of chronic changes.
- Pleomorphism is often suggestive of malignancy. Paradoxically, in the context of radiation, less pleomorphic (clonal-appearing) cells may be malignant!
DDx:
- Pleomorphic tumours.
- Well-differentiated carcinoma, e.g. postradiation prostatic carcinoma, may go unnoticed in the background of radiation-associated nuclear changes.
- Atypia associated with drugs.
- "Giant cell cystitis" - benign mesenchymal atypia with or without inflammation.
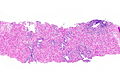
Images
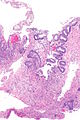
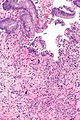
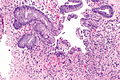
Rectum
Radiation proctitis - low mag. (WC)
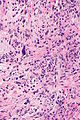
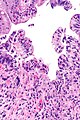
Prostate gland
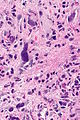
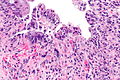
Brain
Glioblastoma with RC (WC/jensflorian)
IHC
- Pankeratin -ve.
- KI-67 low.
Sign out
RECTUM, BIOPSY: - SQUAMOUS MUCOSA WITH MARKED ACUTE INFLAMMATION AND REACTIVE CHANGES. - GRANULATION TISSUE. - LARGE ATYPICAL STROMAL CELLS AND FIBROSIS, COMPATIBLE WITH THE HISTORY OF RADIATION TREATMENT. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
URINARY BLADDER, TRIGONE, BIOPSY: - INFLAMED UROTHELIAL MUCOSA WITH SQUAMOUS METAPLASIA, ULCERATION AND GRANULATION TISSUE FORMATION. - RADIATION CHANGES (STROMA). - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Urinary bladder, biopsy: - Urothelial mucosa with evidence of ulceration (fibrin, necroinflammatory debris), mild stromal atypia and chronic inflammation, compatible with radiation cystitis - Negative for dysplasia - Negative for malignancy
Micro
Scattered rare large atypical cells with a preserved nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio are present. Fibrosis is present.
See also
- Radiation colitis.
- Radiation esophagitis.
- Radiation changes in cervical cytology.
- Radiation changes of the endocervical epithelium.
- Radiation oncology.
- Endometrium post-ablation.