Difference between revisions of "Proton pump inhibitor effect"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
*Due to intake of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). | *Due to intake of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). | ||
**Used to treat [[gastroesophageal reflux disease]]. | **Used to treat [[gastroesophageal reflux disease]]. | ||
Some proton pump inhibitors: | |||
*Omeprazole (LOSEC). | |||
*Dexlansoprazole (DEXILANT). | |||
*Lansoprazole (PREVACID). | |||
*Esomeprazole (NEXIUM). | |||
*Pantoprazole (PANTOLOC). | |||
*Rabeprazole (PARIET). | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Revision as of 21:13, 20 January 2014

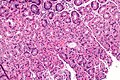
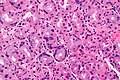
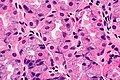
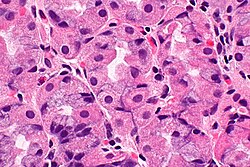
Stomach with PPI effect. H&E stain.
Proton pump inhibitor effect, abbreviated PPI effect, is a change seen in the parietal cells of the stomach due to a drug in the proton pump inhibitor class.
Formally, it is stomach with proton pump inhibitor effect.
General
- Due to intake of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI).
- Used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Some proton pump inhibitors:
- Omeprazole (LOSEC).
- Dexlansoprazole (DEXILANT).
- Lansoprazole (PREVACID).
- Esomeprazole (NEXIUM).
- Pantoprazole (PANTOLOC).
- Rabeprazole (PARIET).
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Parietal cell enlargement - key feature.
- Parietal cells typically bulge into the lumen.
Images
www:
Sign out
- Usually not reported.