Polarization
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.

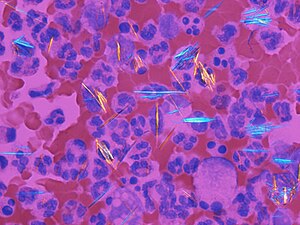
Crystals (gout) and blood cells in polarized light. (WC/Gabriel Caponetti)

Acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma with non-polarized light and polarized light to highlight the oxylate crystals. H&E stain. (WC/Nephron)
Polarization, formally light polarization, in pathology refers to a technique used in light microscopy that makes use of polarized light.
General
- Polarization is a useful characteristic as it is only seen in handful of pathologies.
- In some cases the colour and histomorphology can be specific enough to be diagnostic.
Notable things that polarize
- Amyloid - apple-green birefringence.[1]
- Oxylate crystals.
- Gout crystals - negatively birefringent, yellow when aligned, needle-shaped.[4]
- Pseudogout crystals - positively birefringent, blue when aligned, rhomboid-shaped.[4]
Some other things that polarize
- Dirt.
- Collagen.
See also
References
- ↑ Cornejo, KM.; Lagana, FJ.; Deng, A. (Nov 2015). "Nodular amyloidosis derived from keratinocytes: an unusual type of primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis.". Am J Dermatopathol 37 (11): e129-33. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000307. PMID 26485243.
- ↑ Rosano, TG.; Swift, TA.; Kranick, CJ.; Sikirica, M. (Oct 2009). "Ethylene glycol and glycolic acid in postmortem blood from fatal poisonings.". J Anal Toxicol 33 (8): 508-13. PMID 19874660.
- ↑ Ozer, E.; Canda, T.; Balci, P.; Gökçe, O.. "Calcium oxalate crystals in benign cyst fluid from the breast. A case report.". Acta Cytol 43 (2): 281-4. PMID 10097726.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Yeung, J.C.; Leonard, Blair J. N. (2005). The Toronto Notes 2005 - Review for the MCCQE and Comprehensive Medical Reference (2005 ed.). The Toronto Notes Inc. for Medical Students Inc.. pp. RH6. ISBN 978-0968592854.