Myocarditis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
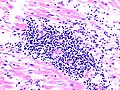
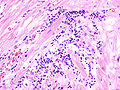
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart.
Idiopathic granulomatous myocarditis is dealt with in a separate article.
General
- Uncommon.
Gross
- Not apparent on gross.
Grossing:
- Requires 10 sections to exclude;[1] sections should include right ventricle and left ventricle.
- It is often missed with five.[2]
Microscopic
Features:
- Inflammation.
- Myocyte necrosis - disputed.[3]
Classification
Classified by the inflammatory cells present:[4]
- Eosinophilic - hypersensitivity myocarditis - most common.
- May be assoc. with peripheral blood eosinophilia.[5]
- Lymphocytic - viral, autoimmune.
- Granulomatous - infectious, idiopathic.
- Neutrophilic.
- Reperfusion (associated with myocardial infarction).
Images
www
See also
References
- ↑ KC. 1 October 2010.
- ↑ Kubo, N.; Morimoto, S.; Hiramitsu, S.; Uemura, A.; Kimura, K.; Shimizu, K.; Hishida, H. (1997). "Feasibility of diagnosing chronic myocarditis by endomyocardial biopsy.". Heart Vessels 12 (4): 167-70. PMID 9559966.
- ↑ Baughman, KL. (Jan 2006). "Diagnosis of myocarditis: death of Dallas criteria.". Circulation 113 (4): 593-5. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.589663. PMID 16449736.
- ↑ http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1612533-overview
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Amini R, Nielsen C (2010). "Eosinophilic myocarditis mimicking acute coronary syndrome secondary to idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome: a case report". J Med Case Reports 4: 40. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-4-40. PMC 2830978. PMID 20181108. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2830978/.