Difference between revisions of "Leukemia"
m (subclude CML) |
(some rearranging + classification) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Acute leukemia-ALL.jpg | thumb|right|A bone marrow of an individual with precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. [[Wright stain]]. (WC)]] | [[Image:Acute leukemia-ALL.jpg | thumb|right|A bone marrow of an individual with precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. [[Wright stain]]. (WC)]] | ||
The | The term '''leukemia''' is broadly used to refer to any haematological malignancy where the neoplastic cells in the circulation are the prominent feature. It is generally only seen by anatomical pathologists only in countries where hematopathology reporting is done by anatomical pathologists rather than hematologists. | ||
Lymphoma is discussed in the ''[[lymphoma]]'' article, and overlaps somewhat with leukemia as the clear distinction between the two is historical | Lymphoma is discussed in the ''[[lymphoma]]'' article, and overlaps somewhat with leukemia as the clear distinction between the two is somewhat arbitrary and historical:<ref>{{Ref PCPBoD8|314}}</ref> | ||
*Leukemia = involves bone marrow +/- peripheral blood. | *Leukemia = involves bone marrow +/- peripheral blood. | ||
**Classic presentation: infection, bleeding, anemia. | **Classic presentation: infection, bleeding, anemia. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 9: | ||
=Definition= | =Definition= | ||
This varies with the type. | |||
For acute myeloid leukemia, all of the following:<ref name=dg21mar20011>D. Good. 21 March 2011.</ref> | |||
#Morphologic abnormalities. | #Morphologic abnormalities. | ||
#>20% blasts ''or'' recurrent cytogenetic abnormality. | #>20% blasts ''or'' recurrent cytogenetic abnormality. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
*inv(16). | *inv(16). | ||
*t(15;17). | *t(15;17). | ||
=Leukemia classification= | |||
*[[Acute myeloid leukemia]] (AML): | |||
*#AML. | |||
*#AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities. | |||
*#AML from [[MDS]]. | |||
*#AML in the setting of [[Down syndrome]]. | |||
*[[Acute lymphoblastic leukemia]] (ALL): | |||
*#B cell. | |||
*#B cell with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities. | |||
*#T cell (sometimes abbreviated to T-ALL) | |||
*Not to be confused with [[adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma]] (ATLL) | |||
*[[Chronic myeloid leukemia]] (CML) | |||
*[[Chronic lymphocytic leukemia]] (CLL) - usually classified with lymphomas | |||
Rarer leukemias: | |||
*Plasma cell leukaemia | |||
*Mast cell leukemia | |||
=Histomorphologic overview= | =Histomorphologic overview= | ||
| Line 38: | Line 59: | ||
|} | |} | ||
† should be easy to remember as smALL people, i.e. kids, get this type of acute leukemia. | † should be easy to remember as smALL people, i.e. kids, get this type of acute leukemia. | ||
=Algorithms= | =Algorithms= | ||
| Line 49: | Line 69: | ||
*[[Down syndrome]]? | *[[Down syndrome]]? | ||
=Prognosis= | =Prognosis= | ||
| Line 70: | Line 77: | ||
=Specific diagnoses= | =Specific diagnoses= | ||
*[[Acute myeloid leukemia]] | |||
*[[Acute lymphoblastic leukemia]] | |||
*[[Chronic myeloid leukemia]] | |||
*[[Chronic lymphocytic leukemia]] | |||
*[[ | |||
*[ | |||
*[[ | |||
*[ | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 26 May 2018
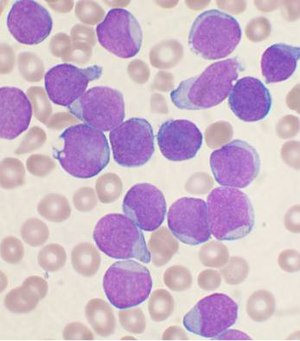
The term leukemia is broadly used to refer to any haematological malignancy where the neoplastic cells in the circulation are the prominent feature. It is generally only seen by anatomical pathologists only in countries where hematopathology reporting is done by anatomical pathologists rather than hematologists.
Lymphoma is discussed in the lymphoma article, and overlaps somewhat with leukemia as the clear distinction between the two is somewhat arbitrary and historical:[1]
- Leukemia = involves bone marrow +/- peripheral blood.
- Classic presentation: infection, bleeding, anemia.
- Lymphoma = discrete mass(es), usu. lymph node.
- Classic presentation: non-tender lymph nodes
Definition
This varies with the type.
For acute myeloid leukemia, all of the following:[2]
- Morphologic abnormalities.
- >20% blasts or recurrent cytogenetic abnormality.
Some recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities:
- t(8;21).
- inv(16).
- t(15;17).
Leukemia classification
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML):
- AML.
- AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities.
- AML from MDS.
- AML in the setting of Down syndrome.
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL):
- B cell.
- B cell with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities.
- T cell (sometimes abbreviated to T-ALL)
- Not to be confused with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL)
- Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) - usually classified with lymphomas
Rarer leukemias:
- Plasma cell leukaemia
- Mast cell leukemia
Histomorphologic overview
| Disease/Feature | Blast size | Auer rods | Granulation of cytoplasm |
| Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | larger | present | present |
| Acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL) | smaller † | none | absent or present |
† should be easy to remember as smALL people, i.e. kids, get this type of acute leukemia.
Algorithms
There is a nice set of algorithms from D. Arber - that were presented at the 2009 USCAP.
Clinical factors in classification
Clinical are important in the classification of leukemia.
- Hx of myelodysplastic syndrome?
- Chemotherapy?
- Down syndrome?
Prognosis
Highly dependent on health care system and treatment available[3]
- 5-year overall survival in children ranges:
- lymphoid leukaemia: 52.4% (Colombia) to 91.6% (Germany)
- acute myleoid leukemia: 33.3% (Bulgaria) to 78.2% (Germany)
Specific diagnoses
- Acute myeloid leukemia
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
See also
References
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 314. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ D. Good. 21 March 2011.
- ↑ Bonaventure, A.; Harewood, R.; Stiller, CA.; Gatta, G.; Clavel, J.; Stefan, DC.; Carreira, H.; Spika, D. et al. (Apr 2017). "Worldwide comparison of survival from childhood leukaemia for 1995-2009, by subtype, age, and sex (CONCORD-2): a population-based study of individual data for 89 828 children from 198 registries in 53 countries.". Lancet Haematol. doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30052-2. PMID 28411119.