Kimura disease
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
| Kimura disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
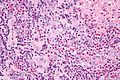
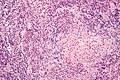
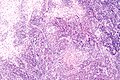
 Kimura disease. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | eosinophils and thick walled blood vessels with hobnailed endothelial cells |
| LM DDx | angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia, drug reaction, infection (parasitic), lymphoma, LCH |
| Site | lymph node, head and neck |
|
| |
| Prevalence | extremely rare |
| Blood work | eosinophilia |
Kimura disease is a rare disease with abundant eosinophils. It may show-up in a lymph node specimen. It is similar to angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia.[1]
General
- AKA eosinophilic lymphogranuloma, Kimura disease.
- Chronic inflammatory disorder - suspected to be infectious.
Clinical:
- Usually neck, periauricular.
- Peripheral blood eosinophilia.
- Increased blood IgE.
Epidemiology
- Males > females.
- Young.
- Asian.
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Angiolymphoid proliferation.
- Eosinophils - abundant - key feature.
DDx:
- Drug reaction.
- Parasitic infection.
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia.
Notes:
- In a lymph node... it may be signed-out as reactive lymphadenitis with follicular hyperplasia and prominent eosinophils, see comment.
- Abundant eosinophils: consider Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
Images
IHC
- Used to rule-out a clonal population, i.e. lymphoma.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1082603-overview. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.
- ↑ Ioachim, Harry L; Medeiros, L. Jeffrey (2008). Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 190. ISBN 978-0781775960.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1098777-diagnosis. Accessed on: 8 August 2010.