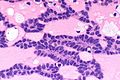
Canalicular adenoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
| Canalicular adenoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
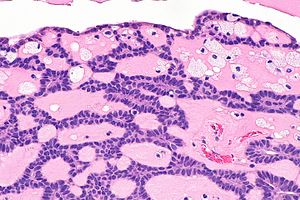 Canalicular adenoma. H&E stain. (WC) | |
|
| |
| LM |
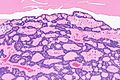
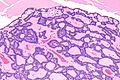
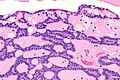
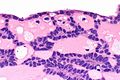
cords of tumour ("canals") with beading (characteristic), cystic spaces/tubules, intraluminal squamous balls (common) |
| Site | salivary gland - usually upper lip or buccal mucosa |
|
| |
| Signs | mass lesion |
| Prevalence | very rare |
Canalicular adenoma is a rare salivary gland tumour.
General
- Exclusively oral cavity.
Clinical:
- Mass lesion.[1]
Gross
- Classically upper lip - may be buccal mucosa or palate.
Note:
- In one large series of 67 cases:[1]
- Upper lip 69% (47/67).
- Buccal mucosa 25% (17/67).
- Palate 6% (4/67).
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Cords of tumour ("canals") with beading - characteristic.
- Cystic spaces/tubules.
- Intraluminal squamous balls - common (~60% of cases).
- Myxoid/bluish stroma.
DDx:
Images
www
IHC
Features:[1]
- S-100 +ve - diffuse and strong.
- Pankeratin +ve - diffuse and strong.
- GFAP +ve - luminal.
- SOX10 +ve - nuclear.
- p16 +ve - luminal squamous balls.
- CK5/6 +ve - luminal squamous balls.
- p63 -ve.
- Nuclei negative, cytoplasm positive.
- Positive in basal cell adenoma.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Thompson, LD.; Bauer, JL.; Chiosea, S.; McHugh, JB.; Seethala, RR.; Miettinen, M.; Müller, S. (Jun 2015). "Canalicular adenoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 67 cases with a review of the literature.". Head Neck Pathol 9 (2): 181-95. doi:10.1007/s12105-014-0560-6. PMID 25141970.