Aspiration pneumonia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of pneumonia.
A special type of aspiration pneumonia is lipoid pneumonia. It is dealt with in the lipoid pneumonia article.
General
- Not associated with microorganisms - though empiric antibiotics are relatively common to cover infectious pneumonias that cannot be excluded easily on clinical grounds.[1]
- Usually seen in the context of a toxin and/or pathology that affects the swallowing and cough reflexes.[2]
Common associations:[2]
- Stroke.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Alcohol intoxication.
Other risk factors:[1]
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Seizure disorder.
- Bowel obstruction.
- Drugs.
- Obesity.
- Labour.
Gross
- More common in the right lung.
- Right main stem bronchus is more vertical.
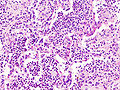
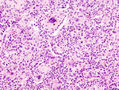
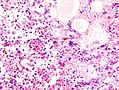
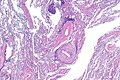
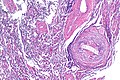
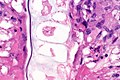
Microscopic
Features:
- Neutrophils.
- Foreign material, e.g. plant matter.
- +/-Foreign body giant cells.
- +/-Microorganisms.
DDx:
Images
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Raghavendran, K.; Nemzek, J.; Napolitano, LM.; Knight, PR. (Apr 2011). "Aspiration-induced lung injury.". Crit Care Med 39 (4): 818-26. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31820a856b. PMID 21263315.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Ohrui, T. (Sep 2005). "Preventive strategies for aspiration pneumonia in elderly disabled persons.". Tohoku J Exp Med 207 (1): 3-12. PMID 16082150.