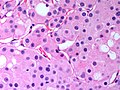
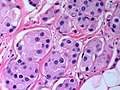
Apocrine carcinoma of the breast
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
| Apocrine carcinoma of the breast | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
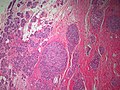
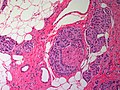
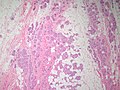
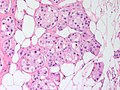
 Apocrine carcinoma of the breast. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | apocrine morphology (cells with prominent nucleoli - may be multiple, abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm) - must be >=90% of tumour, loss of basal cells |
| LM DDx | glycogen-rich clear cell carcinoma of the breast |
| IHC | AR +ve, GCDFP-15 +ve, ER -ve, PR -ve, HER2 +ve/-ve |
| Grossing notes | breast grossing |
| Staging | breast cancer staging |
| Site | breast - see invasive breast cancer |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | poor, worse the ductal carcinoma |
| Clin. DDx | other breast masses |
| Treatment | excision |
Apocrine carcinoma of the breast is a rare form of invasive breast cancer.
General
- Need >=90% apocrine morphology.[1]
- Worse prognosis that invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast in a large series.[2]
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Prominent red nucleoli.
- Often multiple.[3]
- Abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Architecture like invasive ductal carcinomas no special type.
DDx:
- Glycogen-rich clear cell carcinoma of the breast.
- Cutaneous Apocrine Carcinoma
- A possible cutaneous apocrine carcinoma in a patient with a history of mammary apocrine carcinoma is problematic but fortunately a relatively infrequent conundrum.
- Apocrine-like carcinoma - immunoprolife doesn't fit for invasive AC (ER +ve, PR +ve, AR -ve).[2]
Images
www:
IHC
Smaller tumours classically:[4]
Usually:[1]
- ER -ve.
- PR -ve.
- Often HER2 +ve but can be HER2 -ve.[5]
Notes:
- Salivary duct carcinoma and cutaneous adnexal tumours can show a similar IHC profile.
- Apocrine carcioma can be a non-basal type 'triple negative carcinoma'.[6]
- May show different behaviour to other types of triple negative carcinoma.
- May respond to treatments targeting the androgen receptor.[7]
- Be careful when reading the literature in this area - is the author discussing 'molecular apocrine' (ER -ve, AR +ve) or 'morphologic apocrine' carcinoma.
- Many ductal carcinomas, NOS show AR positivity but are often ER +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 O'Malley, Frances P.; Pinder, Sarah E. (2006). Breast Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 217. ISBN 978-0443066801.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Dellapasqua, S.; Maisonneuve, P.; Viale, G.; Pruneri, G.; Mazzarol, G.; Ghisini, R.; Mazza, M.; Iorfida, M. et al. (Apr 2013). "Immunohistochemically defined subtypes and outcome of apocrine breast cancer.". Clin Breast Cancer 13 (2): 95-102. doi:10.1016/j.clbc.2012.11.004. PMID 23245877.
- ↑ O'Malley, FP.; Bane, A. (Jan 2008). "An update on apocrine lesions of the breast.". Histopathology 52 (1): 3-10. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02888.x. PMID 18171412.
- ↑ Honma, N.; Takubo, K.; Akiyama, F.; Sawabe, M.; Arai, T.; Younes, M.; Kasumi, F.; Sakamoto, G. (Aug 2005). "Expression of GCDFP-15 and AR decreases in larger or node-positive apocrine carcinomas of the breast.". Histopathology 47 (2): 195-201. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2005.02181.x. PMID 16045781.
- ↑ Niemeier, LA.; Dabbs, DJ.; Beriwal, S.; Striebel, JM.; Bhargava, R. (Feb 2010). "Androgen receptor in breast cancer: expression in estrogen receptor-positive tumors and in estrogen receptor-negative tumors with apocrine differentiation.". Mod Pathol 23 (2): 205-12. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.159. PMID 19898421.
- ↑ Tsutsumi, Y. (May 2012). "Apocrine carcinoma as triple-negative breast cancer: novel definition of apocrine-type carcinoma as estrogen/progesterone receptor-negative and androgen receptor-positive invasive ductal carcinoma.". Jpn J Clin Oncol 42 (5): 375-86. doi:10.1093/jjco/hys034. PMID 22450930.
- ↑ Safarpour, D.; Tavassoli, FA. (Oct 2014). "A Targetable Androgen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Subtype Hidden Among the Triple-Negative Cancers.". Arch Pathol Lab Med. doi:10.5858/arpa.2014-0122-RA. PMID 25310144.